
Indian Nursing Council
Combined Council Building, Kotla Road, Temple Lane, New Delhi - 110002
Syllabus and Regulations
Diploma in General Nursing & Midwifery
REVISED — 2015

2
Price: ` 150/-
Copyright © 2015 by Indian Nursing Council
Fourth Revision-2015
First Print 2015 - IV
th
Revision
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
reviewed, abstracted, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in
any form or by any means including photocopying without the prior
written permission of the Indian Nursing Council, New Delhi.

3
PREFACE
Indian Nursing Council (INC) is a National statutory body. INC’s main function is to establish Uniform
Standards of nursing education for nursing personnel and to prescribe the syllabus and regulation for various
categories of nursing personnel.
Indian Nursing Council has revised the syllabus and regulations for the General Nursing and Midwifery
training programme. The revision was undertaken by having series of consultations with the various stake
holders. One of the major change in the revised curriculum is duration of the programme. The duration of the
programme has been reduced from 3 ½ years to 3 years, without compromising course content and objectives
of the course, internship has been integrated within the 3 years course.
Another change in the revision of the curriculum is format of the syllabus. The format of the curriculum
changed to include the course description, general objective, learning objectives, course content, number of hours
for each unit, their teaching learning activities and assessment methods. For each subject which had practical
requirements, a detailed description of the area with course description, general objectives, area of practice,
time to be spent in each area with the objectives for each area, the skills to be acquired, the assignments and the
assessment methods are clearly spell out. This will facilitate for the teachers for effectively covering the syllabus
and also guide the nursing teachers to implement the curriculum in totality covering all aspect of the theory and
practical component of the programme.
I am condent that this revised syllabus and regulations will be able to prepare Nurses to provide qualitative
Nursing care in the hospital and also in the community.
I also take this opportunity to acknowledge the contribution Nursing Education Committee Members of
INC, Nursing Experts, Vice-President, INC the then Secretary, INC and Joint Secretary of INC in preparation
of the revised GNM syllabus.
(T. Dileep Kumar)
President
Indian Nursing Council
Ex- Nursing Adviser to Govt. of India
4
5
REGULATIONS
Introduction & Philosophy -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------7
Aims ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
Objectives -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Guidelines and Minimum Requirements to Establish School of Nursing ---------------------------------------- 11
Physical Facilitties ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
Teaching Block ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
Hostel Block ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
Hostel Facilities ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 16
Anti Ragging ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 18
Nursing Teaching Faculty ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 19
Clinical Facilities -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 21
Admission Terms and Conditions ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 24
Curriculum --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 27
Course of Instruction ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 27
Scheme of Examination ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29
CURRICULUM
FIRST YEAR
Bio-Science --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 36
Anatomy and Physiology ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 36
Microbiology --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 39
Behavioural Sciences ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 41
Psychology ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 41
Sociology-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 43
Nursing Foundations ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 45
Fundamentals of Nursing ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 45
First Aid --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 51
Nursing Foundation-Practical -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 53
Community Health Nursing -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 60
Community Health Nursing - I ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 60
Community Health Nursing I - Practical ------------------------------------------------------------------- 63
Environmental Hygiene --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 64
Health Education and Communication skills -------------------------------------------------------------- 66
INDEX
Contents Page No.
6
Nutrition ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 68
English -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------72
Computer Education ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 73
SECOND YEAR
Medical Surgical Nursing – I ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 74
Medical Surgical Nursing – II ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 81
Medical Surgical Nursing I & II Practical ----------------------------------------------------------------- 91
Mental Health Nursing ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 98
Mental Health Nursing - Practical -------------------------------------------------------------------------101
Child Health Nursing --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------102
Child Health Nursing - Practical ---------------------------------------------------------------------------108
THIRD YEAR PART - I
Midwifery and Gynecological Nursing -----------------------------------------------------------------------------110
Midwifery -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------110
Gynecologial Nursing ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------116
Midwifery and Gynaecological Nursing Practical -------------------------------------------------------118
Community Health Nursing - II --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------121
Community Health Nursing II - Practical -----------------------------------------------------------------125
INTERNSHIP (3
rd
Year Part - II)
Nursing Education ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------126
Introduction to Research -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------127
Professional Trends and Adjustment ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------128
Nursing Administration and Ward Management -------------------------------------------------------------------130

7
INTRODUCTION & PHILOSOPHY
Nursing is a profession within the Health Care Sector focused on the care of individuals, families and communities
so they may attain maintain or recover optimal health and quality of life.
Nurses care for individuals of all ages and all cultural backgrounds who are healthy and ill in a holistic manner
based on the individuals physical, emotional, psychological, intellectual, social and spiritual needs. The
profession combines physical sciences, social science and technology in caring for those individuals.
Indian Nursing Council believes in concept of Health laid down by World Health Organisation (WHO) “Health is
a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or inrmity.”
In order to provide qualitative Nursing Care there is a need to train nurses effectively to work as a team member
of health care delivery system. It is therefore their training should involve positive attitudes, knowledge, skills,
professional expertise, latest trends in health care and health care needs of the community and the country as a
whole.
As per the denition of Virginia Avenel Henderson “ The Unique function of the nurse is to assist the individual,
sick or well, in the performance of those activities contributing to health or its recovery (or to peaceful death)
that he would perform unaided if he had the necessary strength, will or knowledge.”
As per the International Council of Nurses “ Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of
individuals of all ages, families, groups and communities, sick or well and in all settings. Nursing includes the
promotion of health, prevention of illness, and the care of ill, disables and dying people. Advocacy, promotion
of a safe environment, research, participation in shaping health policy and in patient and health systems
management and education are also key nursing roles.”
Indian Nursing Council recognized that basic nursing education is a formally recognized programme of students
providing a broad and sound foundation in the behavioural, life and nursing sciences for the practice of nursing
for a leadership role and for the post basic education in specialties for advanced nursing practice. The Country
believes that this basic course in nursing should prepare nurses for occupying rst level positions in nursing
in all kinds of health care settings. The Council recognizes that nursing is a profession which is inuenced by
advances in science and technology, it believes that skills in all aspects of communication are also essential
learning and for the practice of nursing.
The Council also recognizes that the nature of nursing is such that a substantial portion of learning of the
study is acquired in clinical eld(s) of practice. It further recognised the interdependence of nursing to allied
professions and occupations in prevention of diseases, promotion, maintenance and restoration of health.
The Council believes that it has a responsibility in helping the students to develop pride in their profession
besides keeping them abreast with current knowledge and professional trends for a successful career ahead.

8
AIMS
The basic Diploma course in General Nursing and Midwifery is geared to the health needs of the individuals,
family, community and the country at large.
The aims of the Diploma in General Nursing and Midwifery programme are:
1. To prepare nurses with a sound educational programme in nursing to enable them to function as
efcient members of the health team, beginning with the competencies for rst level positions in all
kinds of health care settings.
2. To help nurses develop an ability to co-operate and co-ordinate with members of the health team in
the prevention of disease, promotion of health and rehabilitation of the sick.
3. To help nurses in their personal and professional development, so that they are able to make
maximum contribution to the society as useful and productive individuals, citizens as well as efcient
nurses.
4. To serve as a base for further professional education and specialization in nursing.
5. To prepare nurses to keep pace with latest professional and technological developments and use these
for providing nursing care service.

9
OBJECTIVES
The nurse on completion of this course will be able to:
1. Demonstrate competency in providing health care to individual, sick or well, using nursing process.
- Assess the nursing need of clients from birth of death.
- Plan and carry out appropriate action to meet nursing needs.
- Provide effective nursing care for maintain best possible level of health in all aspects.
- Promote self care in people under their care.
- Apply problem solving techniques in nursing practice.
- Evaluate effectiveness of nursing care.
- Apply problem solving techniques in nursing practice.
- Evaluate effectiveness of nursing care.
2. Apply knowledge from the humanities, biological and behavioral sciences in functioning as a nurse.
3. Function effectively with members of the health team and community applying the knowledge of human
relations and communication skills in her work.
4. Participate as member of the health team in delivery of curative preventive, promotive and rehabilitative
health care service.
5. Mobilize community resources and their involvement in working with the communities.
6. Demonstrate use of ethical values in their personal and professional life.
7. Demonstrate interest in activities of professional organization.
8. Recognize the need for continuing education for professional development.
9. Demonstrate basic skills in teaching patients and giving nursing care to them.
10. Demonstrate basic skills in administration and leadership while working with other members of health
team and community.
11. Assist in research activities.

10
REGULATION

11
GUIDELINES FOR ESTABLISHMENT OF NEw GENERAL
NURSING AND MIDwIFERY SCHOOL OF NURSING
1. Any organization under: (i) Central Government/State Government/Local body (ii) Registered Private
or Public Trust (iii) Missionary or any other organization registered under Society Registration Act (iv)
Company incorporated under section 8 of Company’s act are eligible to establish General Nursing and
Midwifery School of Nursing.
2. Any organization having 100 bedded Parent (Own) hospital is eligible to establish General Nursing
Course.
3. Above organization shall obtain the Essentiality Certicate/No Objection Certicate for the General
Nursing and Midwifery programme from the respective State Government. The institution name
along with Trust Deed/Society address shall be mentioned in No Objection Certicate/Essentiality
Certicate.
4. An application form to establish Nursing programme is available on the website viz., www.
indiannursingcouncil.org, which shall be downloaded. Duly lled in application form with the requisite
documents mentioned in the form shall be submitted before the last date as per the calendar of events
of that year.
5. The Indian Nursing Council on receipt of the proposal from the Institution to start nursing programme,
will undertake the rst inspection to assess suitability with regard to physical infrastructure, clinical
facility and teaching faculty in order to give permission to start the programme.
6. After the receipt of the permission to start the nursing programme from Indian Nursing Council, the
institution shall obtain the approval from the State Nursing Council and Examination Board.
- Before the admission of the students next year institute will submit the renewal/validity form as
per the calendar of events every year. However INC may conduct yearly inspection.
7. Institution will admit the students only after taking approval of State Nursing Council Examination
Board.
Note:
• If, no admission are made for two consecutive academic years then it shall be considered as closed for
the said programme.
• If the institution wants to restart the programme they have to submit the rst inspection fees within 5
years i.e., from the year they did not have admissions. Guidelines of the year wherein institute was rst
permitted will be applicable.
12
PHYSICAL FACILITITIES
Teaching Block:
The School of Nursing should have a separate building/teaching block*. For a School with an annual admission
capacity of 40-60 students, the constructed area of the School should be 20000 square feet.
The School of Nursing can be in a rented/leased building for rst two years. After two years institute shall have
own building in an institutional area. Otherwise Rs.50,000 penalty has to be paid for every year. During the
penalty period institute shall be able to construct own building. If the institution is not able to have their own
building, permission/suitability will be withdrawn and however institution will be given chance to submit the
proposal towards rst inspection with the latest guidelines.
Adequate hostel/residential accommodation for students and staff should be available in addition to the above
mentioned built up area of the Nursing School respectively. The details of the constructed area are given below
for admission capacity of 40-60 students:
S. No. Teaching Block Area (Figures in Sq. feet)
1. Lecture Hall 3 @ 900 = 2700
2. (i) Nursing foundation lab 1500
(ii) CHN & Nutrition Lab 900
(iii) Advance Nursing Skill Lab 900
(iv) OBG and Paediatrics Lab 900
(v) Pre-clinical science lab 900
(vi) Computer Lab 1500
3. Multipurpose Hall 3000
4. Common Room (Male & Female) 1000
5. Staff Room 1000
6. Principal Room 300
7. Vice Principal Room 200
8. Library 1800
9. A.V. Aids Room 600
10. Faculty Room 1800
11. Provisions for Toilets 1000
Total 20000 Sq. Ft.
13
Note:
*1. Nursing Educational institution should be in Institutional area only and not in residential area.
*2. If the institute has non-nursing programme in the same building, Nursing programme should have
separate teaching block.
*3. Shift-wise management with other educational institutions will not be accepted.
*4. Separate teaching block shall be available if it is in hospital premises.
*5. Proportionately the size of the built-up area will increase according to the number of students
admitted.
*6. School and College of nursing can share laboratories, if they are in same campus under same name
and under same trust, that is the institution is one but offering different nursing programmes. However,
they should have equipments and articles proportionate to the strength of admission. And the class
rooms should be available as per the requirement stipulated by Indian Nursing Council of each
programme.
Hostel Block:
Hostel Provision is Mandatory and shall also be owned by the institute within the period of two years
S. No. Hostel Block Area (Figures in Sq feet)
1. Single Room 9000 (50 sq. ft. for each student)
Double Room
2. Sanitary One latrine & One Bath room (for 60 students)
– 600 × 3 = 1800
3. Visitor Room 500
4. Reading Room 250
5. Store 500
6. Recreation Room 500
7. Dining Hall 3000
8. Kitchen & Store 1500
9. Warden’s room 450
Total 17500 Sq. Ft.
Grand Total (total requirement for the nursing programme): - 20000 (Teaching Block) + 17500 (Hostel
Block) = 37500 Sq. Ft.
1. Class rooms
There should be at least three classrooms with the capacity of accommodating the number of students admitted
in each class. The rooms should be well ventilated with proper lighting system. There should be built in White
Boards. Also there should be a desk/ dais/a big table and a chair for the teacher and racks/cupboards for keeping
teaching aids or any other equipment needed for the conduct of classes.

14
2. Laboratories
There should be at least Six laboratories as listed below:-
1 Nursing Practice Laboratory
2 Community Health Nursing & Nutrition Laboratory
3 Advance Nursing Skill Laboratory
4 Computer Laboratory
5 OBG & Paediatric Laboratory
6 Pre Clinical Sciences Laboratory
a) Nursing Practice Laboratory: There should be demonstration beds with dummies, mannequins in
proportion to the number of students practicing a nursing procedure at a given point of time (the desired
ratio being 1 bed: 6 practicing students).
It should be fully equipped with built-in-cupboards and racks. Wash-basins with running water supply,
electric tting, adequate furniture like table, chairs, stools, patient lockers footsteps etc. Sufcient
Necessary inventory articles should be there i.e. at least 10-12 sets of all items needed for the practice
of nursing procedure by the students.
b) Community Practice & Nutrition Laboratory: It should have all required articles needed for practicing
nursing procedures in a community set-up. The laboratory should give appearance of that of a rural
setting, with community maps, records put up on display & cupboards.
It should also have facilities for imparting basic knowledge of various methods of cooking for the healthy
as well as for the sick. The furnishing and equipment should include work-tables, cooking cutlery, trays,
plates, dietetic scales, cooking utensils, microwave, racks/ shelves, refrigerator, pressure cookers, mixie
and cupboards for storage of food items. The food items shall be purchased for the conduct of practical
classes as and when required. Sets of crockery and cutlery for preparation, napkins for serving and
display of food also should be there.
c) Computer Laboratory: It can be shared with other departments.
d) OBG &Pediatric Laboratory: Laboratory should have equipment and articles as mentioned in laboratory
equipments and articles.
e) Advance Nursing Skill Laboratory: There should be simulators used teach, practice & learn advance
skills e.g., administration of tube- feeding, tracheostomy, gastrostomy etc. I/V injection, BLS, newborn
resuscitation model, etc. The lab should have computers, internet connection, monitor used in Critical
Care Units.
f) Pre-clinical Science lab: It is the laboratory of Biochemistry, Anatomy, and Microbiology. The laboratory
articles mentioned in the laboratory equipment & articles shall be available.
3. Multipurpose Hall
It can be utilized for hosting functions of the college, educational conferences/ workshops, CNES examinations
etc. It should have proper stage with green room facilities. It should be well –ventilated and have proper lighting
system. There should be arrangements for the use of all kinds of basic and advanced audio-visual aids.
15
4. Library
There should be a separate library in the school. It should be easily accessible to the teaching faculty and the
students, during school hours and extended hours also.
It should have comfortable seating arrangements for half of the total strength of the students and teachers in the
school.
There should be separate budget for the library. The library committee should meet regularly for keeping the library
updated with current books, journals and other literature. Internet facility should be provided in the library.
The library should have proper lighting facilities and it should be well-ventilated. It should have a cabin for
librarian with intercom phone facility.
There should be sufcient number of cupboards, books shelves and racks with glass doors for proper and safe
storage of books, magazines, journals, newspapers and other literature. There should be provision for catalogue-
cabinets, racks for student bags etc., book display racks, bulletin boards and stationery items like index cards,
borrowers cards, labels and registers. Current books, magazines, journals, newspaper and other literature should
be available in the library.
A minimum of 500 of different subject titled nursing books (all new editions), in the multiple of editions, 3
kinds of nursing journals, 3 kinds of magazines, 2 kinds of newspapers and other kinds of current health related
literature should be available in the library.
There should be a separate record room with steel racks, built-in shelves and racks, cupboards and ling cabinets
for proper storage of records and other important papers/ documents belonging to the college.
5. Ofces Requirements
a. Principal’sOfce
There should be a separate ofce for the Principal with attached toilet and provision for visitor’s room. Independent
telephone facility is a must for the Principal’s ofce with intercom facility connected/linked to the hospital and
hostel.
b. OfceforVice-Principal
There should be a separate ofce for the Vice-Principal with attached toilet and provision for visitor’s room.
Independent telephone facility is a must for Vice-principal’s ofce with intercom facility connected/linked to
the hospital and hostel.
c. FacultyRoom
There should be adequate number of ofce rooms in proportion to the number of teaching faculty. One ofce
room should accommodate 2 teachers only. Separate toilet facility should be provided for the teaching faculty
with hand washing facility. There should be a separate toilet for male teachers.
d. StaffRoom
One separate ofce room for the ofce staff should be provided with adequate toilet facility. This ofce should
be spacious enough to accommodate the entire ofce staff with separate cabin for each ofcial. Each ofce room
should be adequately furnished with items like tables, chairs, cupboards, built –in racks and shelves, ling cabinets
and book cases. Also there should be provision for equipments like photocopy, computers and telephone.
16
6. Common Rooms
Common rooms should be provided. One for the teaching faculty, one for the student and one for the ofce
staff. Sufcient space with adequate seating arrangements, cupboards, lockers, cabinets, built-in-shelves and
racks should be provided in all the common rooms. Toilet and hand washing facilities should be made available
in each room.
7. Audio-Visual Aids Room & Store Room
This room should be provided for the proper and safe storage of all the Audio-Visual Aids. The School should
possess all kind of basic as well as advanced training aids like chalk boards, overhead projectors, slide and
lm-strip projector, models specimen, charts and posters, T.V. & V.C.R., Photostat machine, tape recorder and
computers, LCD, laptop.
It should be provided to accommodate the equipments and other inventory articles which are required in the
laboratories of the college. This room should have the facilities for proper and safe storage of these articles and
equipments like cupboards, built-in-shelves, racks, cabinets, furniture items like tables and chairs. This room
should be properly lighted and well-ventilated.
8. Other Facilities
Safe drinking water and adequate sanitary/toilet facilities should be available for both men and women separately
in the school. Toilet facility to the students should be there along with hand washing facility.
9. Garage
Garage should accommodate a 50 seater vehicle.
10. Fire Extinguisher
Adequate provision for extinguishing re should be available as per the local bye-laws.
11. Playground
Playground should be spacious for outdoor sports like Volleyball, football, badminton and for Athletics.
Hostel Facilities:
There should be a separate hostel for the male and female students. It should have the following facilities.
1. Hostel Room
It should be ideal for 2 students. The furniture provided should include a cot, a table, a chair, a book rack, a
cupboard or almirah for each student.
2. Toilet and Bathroom
Toilet and bathroom facilities should be provided on each oor of the students hostel. Geysers in bathroom and
wash basins should also be provided.

17
3. Recreation
There should be facilities for indoor and outdoor games. There should be provision for T.V., radio and video
cassette player.
4. Visitor’s Room
There should be a visitor room in the hostel with comfortable seating, lighting and toilet facilities.
5. Kitchen & Dining Hall
There should be a hygienic kitchen and dining hall to seat at least 80% of the total students strength at one time
with adequate tables, chairs, water coolers, refrigerators and heating facilities. Hand washing facilities must be
provided.
6. Pantry
One pantry on each oor should be provided. It should have water cooler and heating arrangements.
7. washing & Ironing Space
Facility for drying and ironing clothes should be provided in each oor.
8. warden’s Room
Warden should be provided with a separate ofce room besides her residential accommodation. Intercom facility
with school & hospital shall be provided.
9. Telephone facility accessible to students in emergency situation shall be made available.
10. Canteen
There should be provision for a canteen for the students, their guests, and all other staff members.
11. Transport
School should have separate transport facility under the control of the Principal. 25 and 50 seats bus is preferable
and number of transport shall be as per students strength.
Staff for the Hostel
1. Warden (Female) -3: Qualication- B.Sc. Home Science or Diploma in Housekeeping/Catering. Minimum
three wardens must be there in every hostel for morning, evening and night shifts. If number of students
are more than 150, one more warden/ Asst. Warden/ House keeper for every additional 50 students.
2. Cook-1: For every 20 students for each shift.
3. Kitchen & Dining Room helper- 1: For every 20 students for each shift.
4. Sweeper-3
5. Gardener-2
6. Security Guard/ Chowkidar-3

18
ANTI RAGGING
BUDGET
1. Notice/Circular for prohibition of Ragging shall be available on
- Notice Boards
- Admission Brochure/Prospectus
2. Display Posters/Charts on Prohibition of Ragging in common places.
3. Constitute :-
- Anti- ragging committee with name designation & Telephone no.
- Anti- ragging squad
4. Leaet given to fresher’s students to detail out the telephone no. mentioned to whom to approach in
case of ragging including Anti ragging committee/squad addresses and telephone numbers.
5. Constituting a mentoring cell consisting of students volunteering to be mentors for fresher’s (one mentor
of six fresher’s and one mentor of a higher level for six mentors of the lower level.)
6. Online Afdavit (1) by the student (2) by the parent shall be taken as per the UGC notication from
time to time.
7. Display at multiple places- notices, common rooms, canteens, classrooms, library, toilets, corridors etc.
Anti-ragging help line for students.
8. Complaint box placed at places accessible to students.
In the overall budget of the Institution, there should be provision for school budget under a separate head.
Principal of the school of Nursing should be the drawing and disbursing ofcer.
19
NURSING TEACHING FACULTY
The Principal should be the administrative head of the school. He/She should hold qualication as laid down by
INC. The Principal should be the controlling authority for the budget of the school and also be the drawing and
disbursing ofcer. The Principal and Vice- Principal should be Gazetted ofcers in Government Schools and of
equal status (though non-Gazetted) in non-government Schools.
Qualication of Teaching Staff for General Nursing and Midwifery programme with 40 students
intake:
Ratio of Female and Male Nursing Teachers in School Programme
• For every 7 female nursing teacher there shall be 3 male nursing teacher i.e. 7:3 female to male
nursing teacher ratio.
[i.e., maximum of 30% will be male] it does not direct that female teachers to be replaced by male.
The following is for 60 students intake:
S. No. Teaching faculty Qualication & Experience No. Required
(i) Principal M.Sc. Nursing with 3 years of teaching experience
or B.Sc. Nursing (Basic) / Post Basic with 5 years
of teaching experience.
1
(ii) Vice-Principal M.Sc. Nursing or B.Sc. Nursing (Basic) / Post Basic
with 3 years of teaching experience.
1
(iii) Tutor M.Sc. Nursing or B.Sc. Nursing (Basic/Post Basic) or
Diploma in Nursing Education and Administration
with 2 years of professional experience.
16
Total 18
Note:
• Teacher student ratio should be 1:10 on sanctioned strength of students.
• One of the Tutors need to stay at the community health led by rotation.
• The salary structure of the teaching faculty in private Schools of Nursing should not be less than what
is admissible in the schools of the nursing under State/Central Government.
• Nursing service personnel should actively participate in instruction, Supervision, guidance and evaluation
of student in the clinical and eld/ community practice areas. The teaching faculty of the School of
nursing should work in close coordination with nursing service personnel.
• The teaching faculty of the school and the nursing service personnel should be deputed to attend short
term educational courses/ workshops/ conferences etc. to update their knowledge.
• It is mandatory for school authorities to treat teaching faulty of the school of nursing on duty when
nominated/ selected for the purpose of examination or inspection or inspection by the Council.
• All nursing faculty including Principal shall spend at least four hours each day in the clinical area for
clinical teaching and / or supervision of care by the students.

20
• 50% of the non-nursing subjects should be taught by the nursing teachers. However, it will be
supplemented by the external faculty who are doctors or candidates having PG Qualication in the
requisite subject. Nursing teachers who are involved in non-nursing subjects shall be examiners
for the programme.
EXTERNAL FACULTY
Besides the regular teaching faculty in the school of Nursing, there should be provision for external lectures
for teaching the students. They should possess the desired qualication in the respective subjects which are to
be taught. Remuneration of these external lecturers is to be paid as per the institute/ govt. policy. The external
Faculty may comprise Medical Faculty and Scientists, General Educationist including teaching experts in English,
computer Education. Physical Education/ Yoga, Psychologists, Sociologists, Health Economist/ Statistician,
Nutritionist.
School Management Committee
Following members should constitute the Board of management of the school.
Principal Chairperson
Vice- Principal Member
Tutor Member
Chief Nursing Ofcer/ Member
Nursing Superintendent
Administrative staff for School of Nursing Member
Additional Staff for School of Nursing
Stenographer/Personal Assistant One Should have
Senior Clerk cum Cashier/ Accountant One Knowledge of
Junior Clerk cum Typist One computer
Librarian One
Laboratory Attendant One
Chowkidar/ Watchman Two
Driver One for each Vehicle
Cleaner One for each Vehicle
Peon Three
Sweeper/ Safai Karmachari Two
Machine (Duplicating/ Xerox) Operator One
NB: Provision should be made to have leave reserve staff in addition to the regular staff according
to rules

21
I. Own Hospital: School of nursing should have a 100 bedded Parent (Own Hospital).
II. Additional afliation of hospital:
If all the required learning experience are not available in the parent hospital, the students should be sent to
afliated hospital/ agencies/ Institutions where it is available.
i. Criteria for Afliation
The types of experience for which a nursing school can afliate are:
- Community Health Nursing
- Communicable diseases
- Mental Health (Psychiatric) Nursing
- Specialities like Cardiology, Neurology, Oncology Nephrology etc.
ii. The size of the Hospital/Nursing Home for afliation:-
- Should not be less than 100 beds apart from having own hospital.
- Maximum 3 Hospital can be attached with 100 beds each.
The Physical facilities stafng and equipment of the afliated hospitals should be of the same standard as
required in the hospital.
The Nursing Staff of the afiated hospital should be prepared to recognize the instituitional student with student
status as per their educational programme.
III. Distribution of beds in different areas
Medical 45
Surgical 45
Obst. &Gynaecology 45
Pediatrics 30
Ortho 15
Psychiatric 50
IV. Bed Occupancy of the Hospital should be minimum 75%.
V. Other Specialties/Facilities for clinical experience required are as follows:
Major OT
Minor OT
Dental
Eye/ENT
Burns and Plastic
Neonatology with Nursery
CLINICAL FACILITIES

22
Communicable disease
Community Health Nursing
Cardiology
Oncology
Neurology/Neuro-surgery
Nephrology etc.
ICU/ICCU
VI. There should be a variety of patients of all age groups in all the clinical areas where the students are
posted for obtaining the requisite learning experiences.
VII. The Nursing Stafng norms in the afliated Hospital should be as per the INC norms.
VIII. The afliated Hospital should give student status to the candidates of the nursing programme.
IX. Maximum distance of the afliated hospitals should be within 30 kms.
X. 1:3 student patient ratio to be maintained.
XI. For Tribal and hilly area the maximum distance is 50 kms
IftheinstitutionishavingbothGeneralNursingandMidwiferyandB.Sc.(N)programme,itwouldrequire
toensure1:3studentpatientratiobasedonintakeforeachprogramme.
Distribution of Beds
At least one third of the total number of beds should be for medical patients and one third for surgical patients.
The number of beds for male patients should not be less than 1/6th of the total number of beds i.e. at least 40
beds. There should be minimum of 100 deliveries per month. Provision should be made for clinics in health and
family welfare and for preventive medicine.
Stafng
1. Chief Nursing Ofcer (C.N.O) - for 500 Beds and above. (Qualication as for Principal, SON)
2. Nursing Superintendent (N.S)-1 (Qualication as for Principal, SON).
3. Deputy Nursing Superintendent (D.N.S)-1 (qualication as for vice-principle, SON).
4. Assistant Nursing Superintendent (A.N.S)-2 and for every additional 50 beds one more (qualication as for
vice- Principle, SON).
NORMS RECOMMENDED BY EXPERTS COMMITTEE ON HEALTH MANPOWER PRODUCTION AND
MANAGEMNET (RESOLUTION OF FOURTH CONFERENCE OF CENTRAL COUNCIL OF HEALTH
AND FAMILY WELFARE, ON NURSING, 1995).
Categories Requirements
1. Nursing Superintendent 1:200 beds
2. Dy. Nursing Superintendent 1:300 beds
3. Departmental Nursing Supervisors/ 7:1000( Plus one
Nursing Sisters additional 100 beds
23
4. Ward Nursing Supervisors/ Sisters 8:200+30% leave
Reserve
5. Staff nurse for wards 1:3 (of 1:9 each Shift)+30% leave Reserve
6. For OPD, blood Bank, X-ray 1:100 OPD Patients
Diabetic Clinic CSR etc. (1 bed:5 OPD Patients)+30% leave Reserve.
7. For Intensive Care Unit 1:1 (of 1:3) for each
(8beds ICU for 200 beds) (shift +30% leave Reserve)
8. For specialized departments 8:200 + 30% leave Reserve
and clinic such as OT, Labour room.
Justication
1. Needs may vary from one hospital to another, Depending on its size and service rendered, more staff
than anticipated will be required.
2. Special attention is needed for supervision of patient care in the evening and night shifts.
3. 30% leave reserve posts are mandatory.
Other point to be considered
a. The staff of the parent hospital should be strictly as per the criteria laid down by INC in terms of doctors,
nurses and paramedical staff.
b. Wards/Area/OPDs/OTs/Clinical departments etc. must have adequate coverage of the staff in all the
shifts to ensure that students are only for attending clinical experience in these areas and not utilized
for service purposes.
c. Continuing/ in-service education programme must be attended by all staff nurses to keep themselves
abreast with latest technologies and sophistication used in day to day patient care in these areas.
Community Health Nursing Field Practice Area
The students should be sent for community health nursing experience in urban as well as rural eld area. Institute
can be attached to primary health centre. A well setup eld teaching centre should be provided with facilities for
accommodation of at least 10-15 students and one staff member at a time. Peon, cook and chowkidar should be
available at health centre. Each school of Nursing should have its own transport facilities and it must be under
direct control Principal. The security of staff and students should be ensured.

24
ADMISSION TERMS AND CONDITIONS
1. Minimum education eligibility criteria for admission to GNM:
• 10+2 with English and must have obtained a minimum of 40% at the qualifying examination and English
individually from any recognized board. Candidates are also eligible from State Open School recognized
by State Government and National Institute of Open School (NIOS) recognized by Central Government.
However Science is preferable.
• 10+2 with English having 40% of marks in vocational ANM course from the school recognized by
Indian Nursing Council
• 10+2 with English having 40% of marks in Vocational Stream-Health care Science from a recognized
CBSE board/State/Centre
• Registered ANM with pass mark.
For foreign nationals
• The entry qualication equivalency i.e., 12th standard will be obtained by Association of Indian
Universities, New Delhi. Institution, State Nursing Council will be responsible to ensure that the
qualication and eligibility will be equivalent to what has been prescribed as above
2. Reservation
a) For disabled candidates: 3% Disability reservation to be considered with a disability of locomotor
to the tune of 40% to 50% of the lower extremity and other eligibility criteria with regard to age and
qualication will be same as prescribed for each nursing programme.
Note: A committee to be formed consisting of medical ofcer authorized by medical board of state
government and a nursing expert in the panel which may decide whether the candidates have the disability
of locomotor of 40% to 50%.
b) 5% of total marks is relaxed for SC/ST candidates
c) Any other reservation as per the State Govt.
Note: Reservation shall be applicable within the sanctioned number of the seats by INC and not above
it.
3. Admission of students shall be once in a year.
4. Students shall be medically t.
5. Minimum age for admission will be 17 years. (as on 31st December of that year) The upper age limit is 35
yrs. For ANM/ for LHV, there is no age bar.
Admission / Selection Committee
This committee should comprise of:
- Principal Chairperson
- Vice-Principal
25
- Senior Tutor
- Chief Nursing Ofcer or Nursing Superintendent
ADMISSION STRENGTH
Admission / Intake of candidates shall be as per sanctioned strength permitted by INC.
Health Services
There should be provisions for the following health services for the students.
(a) An annual medical examination.
(b) Vaccination against Tetanus, hepatitis B or any other communicable disease as considered necessary.
(c) Free medical care during illness.
(d) A complete health record should be kept in respect of each individual student. The question of continuing
the training of a student, with long term chronic illness, will be decided by the individual school.
Records
Following are the minimum records which needs to be/should be maintained in the school
a) For Students
1. Admission record
2. Health record
3. Class attendance record
4. Clinical and Field Experience record
5. Internal assessment record for both theory and practical
6. Mark Lists (State Council/Board Results)
7. Record of extracurricular activities of student (both in the school as well as outside)
8. Leave record
9. Practical record books – Procedure book and Midwifery record book to be maintained as prescribed by
INC
b) For each academic year, for each class/batch
1. Course contents record (for each subjects)
2. The record of the academic performance
3. Rotation plans for each academic year
4. Record of committee meetings
5. Record of the stock of the school
6. Afliation record
7. Grant-in-aid record (if the school is receiving grant-in-aid from any source like state Govt. etc.)
8. Cumulative record.
26
Record of educational programmes organized for teaching faculty and student, both in the school as well as
outside.
Annual reports (Record) of the achievement of the school prepared annually.
School of nursing should possess detailed and up-to-date record of each activity carried out in the school.
Transcript
All institutions to issue the transcript upon completion of the course and to submit only one single copy of
transcript per batch to respective State Nursing and Midwifery Registration Council.
27
CURRICULUM
Duration
Course duration = 3 Years
Weeks Available = 52 weeks
Vacation = 4 weeks
Examination (including preparatory) = 2 weeks
Available weeks = 46 weeks
Hours per week = 40 hours
Hours available per academic year (1st & 2nd Year) = 1840 (46 wks × 40 hours) X 2=3680
Hours available for 3rd Year (Part I) = 960 (24 wks × 40 hours)
Internship (Part II) = 1248 (26 wks × 48 hours)
3
rd
Year 2 weeks vacation
2 weeks Examination
Total = 5888 hours
Course of Instruction
FIRST YEAR
Subjects Theory (hours) Practical (hours)
Bio Sciences
- Anatomy & Physiology.
- Microbiology
120
90
30
Behavioral Sciences
- Psychology
- Sociology
60
40
20
Nursing Foundations
- Fundamentals of Nursing.
- First aid
210
190
20
200 (lab) 680(clinic)
(22 weeks)
Community Health Nursing
180
320
8 weeks
- CHN-I 80
- Environmental Hygiene 30
- Health Education & Communication Skills 40
- Nutrition 30
28
Subjects Theory (hours) Practical (hours)
English
30
-
Computer Education
15
15
Co-curricular activities
10
-
TOTAL
625 (16 wks) 1215 (30 wks)
1840
Subjects Theory (hours) Practical (hours)
Medical Surgical Nursing-I 120
800 (20 wks)
Medical Surgical Nursing -II 120
Mental Health Nursing 70 320 (8wks)
Child Health Nursing 70 320 (8wks)
Co-curricular activities 20 -
TOTAL
400 (10 weeks) 1440 ( 36 weeks)
1840
SECOND YEAR
THIRD YEAR Part-I
Subjects Theory (hours) Practice (hours)
Midwifery &Gynaecological
Nursing
140 560 (14 wks)
Community Health Nursing-II 90 160 (4 wks)
Co-curricular 10 -
TOTAL
240 hours (6 weeks) 720 hours (18 weeks)
960
THIRD YEAR Part-II (Integrated supervised Internship)
Theory Subjects Theory (hours)
Nursing Education 20
Introduction to Research and statistics 30
Professional Trends & Adjustments. 30
Nursing Administration & Ward Management 40
TOTAL 120 (2 weeks)
29
Clinical Areas Clinical Hours/ weeks *
Medical Surgical Nursing 288(6 wks)
Community Health Nursing 288(6 wks)
Child Health Nursing 96(2 wks)
Midwifery and Gynaecological Nursing 384(8 wks)
Mental Health Nursing 96(2 wks)
TOTAL 1152 (24 weeks)
Night duty should be given in clinical area(s) in rotation
*43 hours per week for clinical and 5 hours per week for theory.
The students posted in the clinical areas should be accompanied by teaching faculty of the school.
The same practice must be followed when student are posted for requisite clinical experience to afliated
Hospital/Agency /Institution.
The Nursing teachers must actively participate in supervising, guiding and evaluating students in the hospital
wards, health centers and in the community.
1:10 teacher student ratio to be maintained during the supervised clinical practice
SUMMARY OF TOTAL CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
Area 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year –I 3rd Year –II
(Internship)
Nursing Foundation 880 (22) - - -
Community Health Nursing 320 (8) - 160 (4) 288 (6)
Medical Surgical Nursing - 800 (20) - 288 (6)
Mental Health Nursing - 320 (8) - 96 (2)
Child Health Nursing - 320-(8) - 96 (2)
Midwifery and Gynaecological Nursing - - 560 (14) 384 (8)
Total 1200 1440 720 1152
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION:
FIRST YEAR
Paper Subjects Total
Marks
Internal
Assessment
Council/
Board
examination
weightage Duration of
Examination
(Hrs.)
I. Bio Sciences
- Anatomy & Physiology.
- Microbiology
100 25 75
65%
35%
3
30
Paper Subjects Total
Marks
Internal
Assessment
Council/
Board
examination
weightage Duration of
Examination
(Hrs.)
II. Behavioral Sciences
- Psychology
- Sociology
100 25 75
65%
35%
3
III. Foundation of Nursing
- Fundamental of Nursing
- First aid
100 25 75 3
IV. Community Health Nursing
- CHN-I
- Environmental Hygiene
- Health education &
Communication Skills
- Nutrition
100 25 75
50%
10%
25%
15%
3
Practical – I
Fundamental of Nursing
100 50 50
-
SECOND YEAR
Paper Subjects Total Marks Internal
Assessment
Council/
Board
examination
Duration of
Examination
(Hrs.)
I. Medical Surgical Nursing-I 100 25 75 3
II. Medical Surgical Nursing –II 100 25 75 3
III. Mental Health Nursing 100 25 75 3
IV. Child Health Nursing 100 25 75 3
Practical – I
Medical Surgical Nursing
100 50 50 -
Practical-II
Child Health Nursing
100 50 50
Practical-III*
Mental Health Nursing
100 50 50*
Note: * (only school examination, no council/board exam)
*Practical examination for psychiatric nursing is to be conducted at the place of clinical
experience at the end of clinical instruction by school, itself and marks shall be sent to the
council/board.
31
THIRD YEAR Part-I*
Paper Subjects Total Marks Internal
Assessment
Council/
Board
examination
Duration of
Examination
(Hrs.)
I. Midwifery & Gynecological
Nursing
100 25 75 3
II. Community Health Nursing-II 100 25 75 3
Practical I
Midwifery
100 50 50
Practical – II
Community Health Nursing
100 50 50
*Examination for Part-I will be conducted at the end of Third Year
THIRD YEAR Part-II (School Examination)
Paper Subjects Total
Marks
Term
Assessment
School Exam Duration of
Examination
(Hrs.)
I. Nursing Education and Introduction
to Research and statistics
100 50 50 3
II. Professional Trends & Adjustment,
Nursing administration and Ward
Management
100 50 50 3
Examination guidelines
1. Shall have one regular examination followed by supplementary examination in a year.
2. If a candidate fail they can be promoted to next year
3. A candidate can take any number of attempts with a condition that maximum period allowed is 6
years. However all previous papers need to be cleared before appearing in the nal examination
4. No institution shall submit student average internal marks more than 75% i.e., if 40 students are
admitted in a course than the average score of the 40 students shall not exceed 75%.
Example of 5 students: A=25, B=20, C=22, D=21, E=24
Average score=89.6%
This will not be accepted by the State Nursing Registration Council
5. Minimum pass marks should be 50% in each of the Theory and practical paper separately.
6. Minimum pass marks shall be 40% for English only.
7. Theory and Practical exams for Introduction to Computer to be conducted as School exam and marks
to be send to the SNRC/ Board for inclusion in the mark sheet.
8. A candidate has to pass in theory and practical exam separately in each of the paper.
9. If a candidate fails in either theory or practical paper he/she has to re-appear for both the papers
(Theory and Practical)
32
10. Maximum number of candidates for practical examination should not exceed 20 per days.
11. All practical examination must be held in the respective clinical areas.
12. One internal and one external examiners should jointly conduct practical examination for each
students.
Eligibility for Admission to Examination
A candidate shall be eligible for the admission to the state Council / Board examination if the Principle of the
school certicate that:
(a) She / he has completed not less than eleven months of the course
(b) A candidate must have minimum of 80% attendance (irrespective of the kind of absence) in theory
and practical in each subject for appearing for examination.
Thediplomashallnotbeawardedtothestudenttillshe/hehascompletedtheclinical/eld
requirements.
(c) A Candidate must secure 50% marks in internal assessment separately in each theory and practical.
(d) The record of practical experience is complete.
(The Principal shall send to the Council / board the internal assessment for each subject, i.e. both
theory and practical (S) before the start of the examination along with the examination form).
GRADING OF EXAMINATION
Examination shall be graded on aggregate marks of the entire three years of the training programme, as
follows:
Distinction - 80% and above
First Division - 70% to 79%
Second Division - 60% to 69%
Pass - 50% to 59%
THEORY EXAMINATION
1. Nursing teacher with minimum ve years of teaching experience (recent) in a particular subject may
be appointed as paper setters and examiners for that particular subject only.
2. Question paper should have a combination of essay, short answer and objective type question as
detailed in the content
3. All units of a subject and sub-subject should be given due weightage in accordance with the
instructional hours prescribed.
PRACTICAL EXAMINATION
1. Practical examination is to be conducted in the respective clinical area.
2. Nursing teacher with minimum of ve years of teaching/clinical teaching experience in a particular
subject/clinical area may be appointed as practical examiner.
33
MAINTAINENCE OF PRACTICAL RECORD
The student shall be required to maintain the Practical record book and report of observation visits and diary
for assessment must also be used. Marks shall be allotted for each of the following:
a) Case study
b) Case presentation
c) Nursing care plan
d) Maintenance of record books (Procedure Book and Midwifery Record book).
e) Daily diary.
f) Area wise clinical assessment is to be carried out. Minimum two assessments are required in each
clinical area.
Regular record of theory and practical is to be maintained. Task oriented assessment is to be undertaken.
Assessment shall be maintained by teacher for each student each month. This can be checked by the Council/
Board. Principal to sign all the records of examination. It should be displayed on the notice board for the
information of the students.
Each student is required to maintain the record of following assignment in clinical areas in each year:
First Year
a) Nursing care plan - 4 in medical / surgical wards.
b) Daily Diary - 1 each in urban and rural community eld.
c) Health – Talk - 1 each in Urban and rural community eld.
Family Study including - 1 each in Urban and rural community eld.
Health assessment of an - 1 each in Urban and rural community eld.
Individual in the family
Community prole - 1 each in Urban and rural community eld.
Second Year
(a) Medical ward
Nursing Care Plan - 2
Case Study - 1
Case Presentation - 1
Drug Study - 1
(b) Surgical ward
Nursing Care Plan - 2
34
Case Study - 1
Case Presentation - 1
Drug Study - 1
(c) Psychiatry ward
Nursing Care Plan - 1
Case Study - 1
Case Presentation - 1
Drug Study - 1
Process Recording - 2
Mental Status examination - 4
(d) Pediatric ward
Nursing Care Plan - 2
Case Study - 1
Case Presentation - 1
Drug Study - 1
Observation Report (New born) - 2
Third Year
(a) Midwifery and Gynaecological ward.
Nursing Care Plan - 2+1
Case Study - 1+1
Case Presentation - 1+1
Drug Study - 1+1
(b) Daily Diary Urban & Rural Community eld
Health Talk - 2 each
Family Health Nursing care Plan - 2 each
Group Project - 1 each
In addition to above, each student shall maintain a procedure book and midwifery case book signed by
concerned / supervisor and Principle which is to be presented to examiner each year.
The above assignments are to be evaluated by concerned teachers for the purpose of internal assessment and
shall be presented to the external examiner in a compiled form and it should be duly signed by her and should
be stamped as cancelled after practical examination.

35
CURRICULUM
36
Placement- FIRST YEAR Time: Theory- 120 hours
Anatomy and Physiology-90 hours
Microbiology- 30 hours
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
Course Description
This course is designed to help students gain knowledge of the structure and function of the human body and
recognize any deviation from normal health in order to render effective nursing services.
General Objective
Upon completion of the course, the student shall be able to:
1. Describe in general the structure and functions of the human body.
2. Describe in detail the structure and functions of the different organs and systems in the human body.
3. Apply the anatomical and physiological principles in the practice of nursing.
Total Hours – 90
Unit No. Learning
Objectives
Content Hr. Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Dene and
spell various
anatomical terms.
Introduction to anatomical terms
organization of the human body
a) Anatomical terms
b) Systems and cavities of the human
body
4 Lecture cum
Discussions.
Explain using
charts
Record book
Short answer
questions
Objective type
II. Describe different
organs of the
body, systemic
function and their
inter-relationship.
Introduction to the detailed
structure of the body
a) The cell: Structure, reproduction
and function
b) Tissues including membranes and
glands : types, structure and
functions
c) Body cavities and their contents
6 Lecture cum
Discussions.
Explain using
microscopic
slides, Skeleton
and torso
Short answer
questions
Objective type
III Describe the
composition of
blood and its
functions.
Blood
a) Composition and formation of
blood
b) Functions of blood
c) Blood clotting, blood grouping and
cross matching
d) Blood products and their use.
6 Lecture cum
Discussions.
Explain using
microscopic
slides
Short answer
questions
Objective type
Essay type
BIO-SCIENCE
37
Unit No. Learning
Objectives
Content Hr. Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
Demonstration of
blood grouping
and cross-
matching, Hb
estimation
IV. Describe the
structure and
functions of heart
and blood vessels
The Circulatory System
a) Heart : Structure, functions
including conduction system and
cardiac cycle
b) Blood vessels : Types, Structure
and position
c) Circulation of blood
d) Blood pressure and pulse
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, models
and specimen
Short answer
questions
Objective type
Essay type
V. Describe structure
and functions of
lymphatic system
The Lymphatic system
- Structure and function of lymph
vessels, Lymph nodes and lymph
circulation, lymphatic tissue -
spleen and thymus
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts and models
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
VI. Describe the
structure and
functions of
respiratory
system
The Respiratory system
a) The structure and functions of
respiratory organs
b) The physiology of respiration
c) Characteristics of normal
respiration and deviation.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain
using charts
and models,
specimens
Demonstration of
spirometry
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
VII. Describe the
structure and
function of
digestive system
The Digestive system
a) Structure and functions of the
alimentary tract and is accessory
organs.
b) The process of digestion,
absorption and metabolism of food
constituents.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, models
and videos
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
VIII. Describe the
structure and
functions of
organs of
Excretory system.
The Excretory system
a) Structure and functions of the
kidney, ureters, urinary bladder,
and urethra
b) Formation and composition of
urine.
c) Fluid and electrolyte balance
d) Structure and functions of the skin.
e) Regulation of the body
temperature.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, slides
models and
videos
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
38
Unit No. Learning
Objectives
Content Hr. Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
IX. Describe the
structure and
functions of
endocrine glands.
The Endocrine system
- The structure and functions of
the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid
and adrenal glands, pancreas (islets
of Langerhans), ovaries and testes
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts and models
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
X. Describe the
structure and
functions of
male and female
reproductive
system and
accessory organs
The Reproductive system
a) Structure and functions of the
female reproductive system
b) Process of menstrual cycle,
reproduction and menopause
c) Structure and functions of breasts
d) Structure and functions of the male
reproductive system
e) Reproductive health
8 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, videos,
models and
specimens
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
XI. Describe the
structure and
functions of
Nervous system.
The nervous system
a) Types of nerves- structure and
functions
b) Brain and cranial nerves.
c) Spinal cord and motor and
sensory pathways of the spinal
cord, autonomic nervous system.
10 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts and models
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
XII. Describe the
structure and
function of
sensory organs
The sense organs
a) Skin, eye, ear, nose and tongue
b) Physiology of vision, hearing,
smell, touch, taste and equilibrium.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, videos and
models
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
XIII. Describe the
structure and
functions of
skeletal system.
The Skeleton
a) Formation and growth of bones
b) Tendons, ligaments and cartilages
c) Classication of bones, joints
d) Joint movement
e) Axial and appendicular skeleton
8 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, models
and skeleton
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
XIV Describe structure
and functions of
Muscular system.
The Muscular System
a) Type, structure and functions of
muscle
b) Origin, Insertion, and action of
muscles
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts, slides and
models
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type

39
MICROBIOLOGY
Course Description
This course is designed to help students gain knowledge and understanding of the characteristics and
activities of micro- organisms, how they react under different conditions and how they cause different
disorders and diseases. Knowledge of these principles will enable student to understand and adopt practices
associated with preventive and promotive health care.
General Objectives
Upon completion of the course, the students shall be able to:
1. Describe the classications and characteristics of micro-organisms
2. List the common disease producing micro-organisms
3. Explain the activities of micro-organism in relation to the environment and the human body.
4. Enumerate the basic principles of control and destruction of micro-organisms.
5. Apply the principles of microbiology in nursing practice.
Total Hours – 30
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Describe evolution of
microbiology and its
relevance in nursing.
Introduction
a) History of bacteriology and micro-
biology.
b) Scope of microbiology in Nursing
3 Lecture cum
discussions.
Objective type
Short answers
II Classify the different
types of micro
organism.
Describe the normal
ora and the common
diseases caused by
pathogens Explain
the methods to study
microbes
Micro Organisms
a) Classication, characteristics,
(Structure, size, method and rate of
reproduction)
b) Normal ora of the body.
c) Pathogenesis & common diseases.
d) Methods for study of microbes,
culture & isolation of microbes.
8 Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
slides, lms,
videos, exhibits,
models Staining
and xation of
slides.
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
III Describe the sources
of infection and
growth of microbes.
Explain the
transmission of
infection and the
principles in collecting
specimens
Infection and its transmission
a) Sources and types of infection,
nosocomial infection.
b) Factors affecting growth of
microbes.
c) Cycle of transmission of infection
portals of entry, exit, modes of
transfer.
d) Reaction of body to infection,
mechanism of resistance.
e) Collection of specimens.
4 Lecture
Demonstrations
Specimens
Explain using
charts
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
40
IV Describe various
types of immunity,
hypersensitivity
autoimmunity and
immunizing agents
Immunity
a) Types of immunity – innate and
acquired.
b) Immunization schedule.
Immunoprophylaxis (vaccines, sera
etc.)
c) Hypersensitivity and autoimmunity.
d) Principles and uses of serological
tests
5 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Exhibits
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
V Describe the various
methods of control
and destruction of
microbes
Control and destruction of Microbes
a)
Principles and methods of microbial
control
-Sterilization
-Disinfection
-Chemotherapy and antibiotics
-Pasteurization
b) Medical and surgical asepsis
c) Bio-safety and waste management
5 Lecture,
Demonstration
Videos Visit to
the CSSD
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
VI. Demonstrate skill in
handling & care of
microscopes Identify
common microbes
under the microscope
Practical Microbiology
a)
Microscope – Parts, uses, handling
and care of microscope
b) Observation of staining procedure,
preparation and examination of
slides and smears
c) Identication of common
microbes under the microscope for
morphology of different microbes.
5 Lecture,
Demonstrations
Specimens Slides
41
Placement- FISRT YEAR Time- 60 Hours
Psychology- 40 hours
Sociology- 20 hours
PSYCHOLOGY
Course Description
This course is designed to help students understand the dynamics of human behavior and concept of mental
health. This shall enable them to develop positive attitude and good inter – personal relationships in the
practice of nursing in all health care settings.
General Objectives
Upon completion of the course, the students shall be able to:
1. Describe the concept of mental health and psychology.
2. Explain the dynamics of human behavior, personality and learning.
3. Discuss the role of adjustment mechanisms and emotions in health and illness.
4. Demonstrate skills in the application of principle of psychology in nursing practice in all kind of
health care settings.
Total Hours – 40
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I State the concept,
scope and
importance of
psychology.
Introduction
a) Denition, nature and scope of
psychology
b) Importance of psychology for Nurses
2 Lecture cum
discussion.
Short answer
Objective type
II. Describe the
structure of the
mind.
Structure of the mind
a) Conscious, pre-conscious
b) Id, ego and super ego
2 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short answer
Objective type
III. Illustrate the
dynamics of
human behavior.
Describe the
concept of mental
health
Psychology of Human Behavior
a) Basic human needs, dynamics of
behavior, motivation drives
b) Body mind relationship, mental health,
characteristics of mentally healthy
person, emotional control, psychological
problems of patients and relatives.
12 Lecture cum
discussions.
Role play
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
BEHAVIOURAL SCIENCES
42
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
c) Stress and conicts, natural sources and
types of stress and conicts, dealing with
stress and conict, frustration – sources
and overcoming frustration
d) Mental mechanism their uses and
importance
e) Attitudes - meaning, development
changes in attitude, effects of attitudes on
behavior, importance of positive attitude
for the nurse.
f) Habits-meaning and formation.
g) Breaking of bad habits, importance of
good habit formation for the nurse.
IV Describe and
apply the process
of learning,
thinking,
reasoning,
observation and
perception
Learning
a) Nature, types and laws of learning,
b) Factors affecting learning, memory and
forgetting.
Thinking and Reasoning
- Nature and types of thinking, reasoning,
problem solving, importance of creative
thinking for nurse.
Observation and Perception
- Attention, perception, laws of perception,
factors affecting attention and perception,
and errors in perception
13 Lecture cum
discussions.
Roleplay
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
V. Discuss the
concept and
development of
personality.
Personality
a) Meaning, nature and development, types
of personality
b) Assessment of personality importance of
knowledge of personality for the nurse.
c) Characteristics of various age groups –
child adolescent, adult and aged
d) Will and character.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Role play
Psychometric
assessment
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
VI. Discuss the
nature and
measurement of
intelligence.
Intelligence
a) Denition, Meaning, individual
differences in intelligence
b) Mental ability, nature of intelligence and
development
c) Assessment of intelligence
5 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Role play
IQ testing
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
43
SOCIOLOGY
Course Description
This course is designed to help student gain an understanding of sociology in the context of its relevance to
nursing practice.
General Objectives
Upon completion of the course, the students shall be able to:
1. Describe the concept of the family as a social unit and the status of the individual in the family.
2. Explain the dynamics of society and identify common social problems.
3. Demonstrate ability to understand the socio – cultural and economic aspects of the community in the
light of their effects on health and illness.
4. Utilize the knowledge and understanding of sociology in nursing practice.
Total Hours - 20
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
assessment
I Describe the nature,
scope & content
of sociology and
its importance in
nursing
Introduction
a) Denition and scope of sociology
b) Its relationship with other social sciences
c) Uses of sociology for nurses.
2 Lecture cum
discussions
Short answer
Objective type
II Describe the
inuence of the
environment
on individual
development and
the rights and
responsibilities of
the individual in the
society
Individual
a) Review of human growth and
development
b) The socialization process
c) Effect of environment on human growth
and development
d) Rights and responsibilities of the
individual in a democratic society.
2 Lecture cum
discussions
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
III Describe the concept
of family as a social
unit
The Family
a) Denition, characteristics and types of
family.
b) Family cycle and basic needs of family
c) Importance of interdependence of family
members.
d) Important functions of family and their
problems.
e) Types of Marriage, medical and sociology
aspects of marriage.
4 Lecture cum
discussions
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
44
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
assessment
IV Describe about
social groups, social
change, control,
stratication and
social problems
Society
a) Denition and meaning.
b) Social groups - Types, Structure,
intergroup relationship group cycle, group
behavior and group morale.
c) Social change -Meaning, factors affecting
and effect on society and institution
leading to social problems.
d) Social control
e) Social stratication
f) Social problems-Prostitution, crime
divorce, dowry system, juvenile
delinquency, drug addiction alcoholism,
handicapped, over population and slum
g) Social agencies and remedial measures
8 Lecture cum
discussions
Visits to social
institutions
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
V Describe the culture
and characteristics
of community
The Community
a) Community
– Denition and types
– Rural and urban
b) Culture and characteristics
4 Lecture cum
discussions
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
45
Placement- FIRST YEAR Time- 210 hours
Fundamentals of Nursing- 190 hours
First- Aid- 20 hours
FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSINGS
Course Description
This course is designed to help students develop an ability to meet the basic health need of the patients with
regard to nursing care and develop skill in the competencies required for rendering effective patient care.
General Objectives
Upon completion of the course, the students shall be able to:
1 Describe the physical, mental and social adjustment required of a sick individual and his family.
2 Carry out basic nursing techniques and care with the application of sound scientic principle.
3 Explain the concept of comprehensive nursing care.
4 Develop skills in assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation of the nursing care rendered to
the patients.
5 Communicate effectively and establish good interpersonal relationship with the patients, their
relatives and other health team members.
6 Demonstrate skills in observation, recording and reporting.
7 Recognize and utilize opportunities for planning and implementing need based health teaching
programme (s) for individuals, groups, families and communities.
Total Hours - 190
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
I Dene nursing
and explain its
nature, meaning,
scope,ethics and
principles in
nursing.
Identify the
qualities of
Introduction to Nursing
a) Nursing – concept, meaning,
denitions,scope and functions.
b) History of nursing in India
c) Nursing as a profession
d) Nursing professional – qualities and
preparation.
25
Lecture cum
discussions
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
NURSING FOUNDATIONS
46
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
a professional
nurse health care
agencies and its
functions.
Describe the
holistic approach
to nursing and
the determinants
of health and the
effects of illness.
e) Ethics in Nursing-roles and
responsibilities of a nurse.
f) Health care agencies – hospital and
community service – types and
function of hospitals health team.
g) Modern approaches to nursing care
including holistic nursing care
h) Health and Disease
- Denition of health, determinants
of health status.
- Basic human needs
- Illness and its effects on individual
II Describe nursing
care of the
patient/client in
hospital using
nursing process.
Demonstrate skill
in the admission
and discharge
process,
maintenance of
safe environment
and records and
reports
Nursing care of the patient
a) Patient Environment in the hospital:
Patients unit
b) Therapeutic environment
- Physical factors – lighting temperature,
ventilation, humidity, noise, pestilence.
- Safety needs, prevention of
environmental hazard
- Psychosocial and aesthetic factors.
c) Patient’s Adjustment to the Hospital.
- Understanding the patient as a
person, socio-economic, and cultural
background, health status etc.
- Effect of hospitalization on patient and
family.
- Admission, transfer, discharge
procedures
d) Basic Nursing Skills-
- Communication
- Nursing interview
- Recording and reporting
e) Nursing Process
- Meaning and importance
- Assessment, Nursing diagnosis
Planning, Implementation and
Evaluation
- Nursing care plan.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
of maintaining
the records and
reports
Role Play
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
47
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
III Describe
basic needs
of the patient
Demonstrate skill
in meeting basic
care of the patient
Meeting the Basic Needs of a patient
a) Physical needs-
- Comfort, rest, sleep and exercise
–Importance and its promotion
- Body mechanics –moving, lifting,
transferring
- Position and posture maintenance
- Comfort devices
- Beds and bed making – Principles of
bed making, types and care of bed
linen
- Safety devices, restraints and splints
- Exercises – Active and Passive
b) Hygienic needs
- Personal and environmental hygiene
personal
- Nurses note in maintaining personal
and environmental hygiene.
- Care of eyes, nose, ears, hands and
feet.
- Care of mouth, skin, hair and genitalia
- Care of pressure areas, bed sores.
c) Elimination needs
- Health and sickness
- Problems – constipation and diarrhea,
retention and incontinence of urine.
- Nurse’s role in meeting elimination
needs.
- Offering bed-pan and urinal,
- Observing and recording
abnormalities.
- Preparation and giving of laxative,
suppositories, enemas, bowel wash,
atus tube.
- Perineal care, care of patient with
urinary catheter, diapers.
- Maintenance of intake and output
records
d) Nutritional needs
- Diet in health and disease
- Factors affecting nutrition in illness,
- Nurse’s role in meeting patients
nutritional needs.
- Modication of diet in illness.
- Diet planning and serving.
- Feeding helpless patients including
articial methods of feeding.
e) Psychological and spiritual needs
65 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
Assessment using
checklist
48
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
- Importance
- Nurse’s role -Diversional and
Recreational therapy
f) Care of terminally ill and dying patient
- Dying patient’s signs and symptoms
needs of dying patient and family,
- Nursing care of dying-: special
considerations; advance directives,
euthanasia, will, dying declaration,
organ donation etc.
- Medico legal issues
- Care of the dead body
- Care of unit
- Autopsy
- Embalming
IV Describe the
principles of
assessment
demonstrate skills
in assessing the
patient
Assessment of patient/client
a) Physical Assessment
- Importance, principles, methods of
assessment
- Height, Weight, posture
- Head to toe examination.
b) Physiological Assessment
- Vital signs, normal, abnormal
Characteristics, factors inuencing the
variations,
- Observation and collection of
specimens-urine, stool, vomitus and
sputum.
c) Psychological Assessment
- Mood, Intelligence, Emotions Normal
and Abnormal behavior.
14 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
Assessment using
checklist
V Describe the
infection control,
methods in the
clinical setting.
Demonstrate
infection control
practices
Infection control
a) Infection control :
- Nature of infection
- Chain of infection transmission
- Defence against infection: natural and
acquired
- Hospital acquired infection
( nosocomial infection)
b) Concept of asepsis:
- Medical and surgical asepsis
- Isolation precautions , barrier nursing
- Hand washing : simple, hand asepsis,
surgical asepsis (scrub)
- Isolation – source and protection
- Personal protective equipments types,
uses and techniques of wearing and
removing
Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Explain using
manual of
biomedical waste
management of
Government of
India
Demonstration
Videos
Simulation
exercises
Short answers
Essay type
Objective type
49
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
- Decontamination of unit and
equipment
- Transportation of infected patient
-. Standard safety precaution
- Transmission based precautions
c) Bio-medical waste management
- Importance
- Types of hospital wastes
- Hazards associated with hospital waste
- Decontamination of hospital waste
- Segregation and transportation
- Disposal
20
VI Describe
therapeutic
nursing care
Therapeutic Nursing Care
a) Care of patients with respiratory
problems/dyspnea
- Deep breathing and coughing exercises
- O2 inhalation
- Dry and moist inhalation
- Oro nasal suctioning
b) Care of patient with altered body
temperature-Hot and cold Applications
c) Care of patients with Fluid and
Electrolyte imbalance
d) Care of unconscious patient
e) Care of the bed-ridden patient(traction,
fractures etc.)
f) Care of patient with pain
g) Care of patients with body elimination
deviation
30 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
Assessment using
checklist
VIII Explain the
principles,
routes, effects of
administration of
medications
Introduction to clinical Pharmacology
Administrationof medication:
a) General Principles/Considerations
- Purposes of medication
- Principles: Rights, special
considerations, prescriptions, safety
in administering medications and
medication errors
- Drugs forms
- Routes of administration
- Storage and maintenance of drugs and
nurses responsibility
- Broad classication of drugs
- Therapeutic effect, side effect, toxic
effect, allergic reaction, drug tolerance,
drug interactions
- Factors inuencing drug actions
- Systems of drug measurement: metric
system, household measurements.
30 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
Assessment using
checklist
50
Unit.
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
- Converting measurements units:
conversion within one system, between
systems, dosage calculations.
- Terminologies and abbreviations used
in prescription of medications.
b) Oral drug administration: oral,
sublingual, buccal : equipment and
procedure.
c) Parentral:
- General principles
- Types of parentral therapies.
- Types of syringes, needles, canulas and
infusion sets,
- Protection from needle stick injuries,
giving medications with a safety
syringe.
- Routes of parentral therapies:
- Purposes, site equipment, procedure
and special considerations in
giving intradermal, subcutaneous,
intramuscular and intravenous
medications.
- Advanced techniques : epidural,
intrathecal, intraosseous,
intraperitoneal, intrapleural, intra
arterial
- Role of nurse
d) Topical administration: purposes,
site, equipment, procedure, special
considerations for applications to skin
and mucous membrane.
e) Direct application:
- Gargle, throat swab
- Insertion of drug into body cavities :
nasal pack, suppositories / medicated
packing into rectum / vagina
- Instillations: ear, eye, nasal, bladder and
rectal.
- Irrigations: eye, ear, bladder, vaginal
and rectal. Spray: nose and throat
f) Inhalations: nasal, oral, endotracheal,
tracheal (steam, oxygen and
medications) – purposes, types,
equipment, procedure and special
considerations.
g) Recording and reporting of medications
administered.
51
FIRST AID
Course Description
This course is designed to help students develop and understanding of community emergencies and be able to
render rst aid services as and when need arises.
General Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the students shall be able to:
1. Describe the rules of rst aid.
2. Demonstrate skills in rendering rst aid in case of emergencies.
Total Hours - 20
Unit
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Describe the
importance and
principle of rst aid
Introduction
a)
Denition, Aims and Importance of
rst aid
b)
Rules/ General principles of First Aid
c)
Concept of emergency
2 Lecture cum
discussions
Short answer
Objective type
II Demonstrate skill in
rst aid techniques
Procedures and Techniques in First
Aid
a)
Preparation of First Aid kit.
b)
Dressing, bandaging and
splinting(spiral, reverse spiral,
gure of 8 spica, shoulder, hip,
ankle, thumb, nger, stump, single
and double eye, single and double
ear, breast, jaw, capelin), triangle
bandage uses, abdominal binder and
bandage, breast binder, T and many
tail bandage, knots reef, clove.
c)
Transportation of the injured
d)
CPR : Mouth to mouth, Sylvester,
Schafer, External cardiac massage
8 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstration
Videos
Simulation
exercises.
Short answer
Objective type
Return
demonstration
III Describe rst
aid in common
emergencies
First Aid in emergencies
a)
Asphyxia, drowning, shock
b)
Wounds and Bleeding
c)
Injuries to the Bones, Joints and
Muscle - fractures, sprains, strains,
hanging, falls
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Videos
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Return
demonstration
52
Unit
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
d)
Burns and scalds
e)
Poisoning – ingestion, inhalation,
bites and stings
f)
Foreign body in eye, ear, nose and
throat.
IV List various
community
emergencies
and community
resources.
Community Emergencies &
Community Resources
a)
Fire, explosion, oods, earth-quakes,
famines etc
b)
Role of nurses in disaster
management
c)
Rehabilitation
d)
Community Resources
-
Police, Ambulance services
-
Voluntary agencies-local, state
national and international
4 Lecture cum
discussions.
Videos
Mock drill
Simulation
exercise
Videos
Field visit
to voluntary
agencies.
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type

53
Placement: FIRST YEAR Time: Practical – 880 hours
Lab - 200 hours
Clinical – 680 hours
Course Description: This course is designed to help the students to acquire knowledge, attitude and skills in
techniques of nursing and practice them in clinical settings
The nurse on completion of this course will be able to:
q Demonstrate appropriate attitudes and skills in providing comprehensive nursing care to patients based on
nursing process.
• Assess the nursing needs of the clients by collecting complete data, making relevant observation and
analyze the data collected.
• Plan for appropriate nursing care by prioritizing the needs and executing competent nursing actions.
• Implement effective nursing care by integrating scientic principles for maintaining health optimum
• Promote the health of the individual and the community by giving appropriate health teaching.
• Evaluate the patients response to nursing care provided.
• Apply the theoretical knowledge to the appropriate clinical nursing practice.
• Demonstrate skill in the use of problem solving methods in nursing practice.
• Contribute for promotion of health prevention of illness & restoration of health of people by working
with other health team members.
• Gain knowledge of health resources in the community and the country.
• Demonstrate leadership skills in working with health team, community and others in the provision of
health care.
• Recognize the need for continuing education for professional development.
• Demonstrate use of ethical values in their personal and professional life.
• Assist in research activities.
NUSING FOUNDATIONS- PRACTICAL
54
Areas
Time
(Hours)
Objectives Skills Assignments
Assessment
methods
Supervised
practice in
Lab General
Medical
and surgery
wards
200
680
(Minimum
practice
time in
clinical
area)
• Performs
admission
and discharge
procedure
• Prepares
nursing care
plan as per
the nursing
process
format
• Communic
ates
effectively
with patient,
families
and team
members and
• Maintains
effective
human
relations
Hospital admission and
discharge
a) Admission:
• Prepare Unit for new patient
• Prepare admission bed
• Perform admission procedure
• New patient
• Transfer in
• Prepare patient records
b) Discharge/Transfer out
• Gives discharge counseling
• Perform discharge procedure
(Planned discharge, LAMA
and abscond, Referrals
andtransfers)
• Prepare records of discharge/
transfer
• Dismantle, and disinfect
unit and equipment after
discharge/transfer
Perform assessment:
• History taking, Nursing
diagnosis, problem list,
Prioritization, Goals &
Expected Outcomes, selection
of interventions
• Write Nursing Care Plan
• Gives care as per the plan
Communication
• Use verbal and non verbal
communication techniques
Prepare a plan for patient
teaching session
• Practice in
Unit/ hospital
• Write nursing
process records
of patient
• Simulated -1
• Actual - 1
• Role-plays
in simulated
situations on
communi-
cation
techniques-1
• Health talk-1
• Evaluate with
checklist
• Assessment
of clinical
performance
with rating
scale
• Completion
of Practical
record
• Assessment
of nursing
process
records with
checklist
• Assessment
of actual care
given with
rating scale
• Assess role
plays with
the checklist
on comm.
unication
techniques
• Assess health
talk with the
checklist
• Assessment
of comm.-
unication
techniques by
rating scale
55
Areas
Time
(Hours)
Objectives Skills Assignments
Assessment
methods
• Develops
plan for
patient
teaching
• Prepares
patient
reports
• Presents
reports
• Monitors
vital signs
• Performs
health assess-
ment of each
body system
• Provides
basic nursing
care to
patients
write patient report
• Change-of shift reports,
• Transfer reports, Incident
reports etc.
• Present patient report
Vital signs
• Measure, records and
interpret alterations in
body temperature, pulse,
respiration and blood pressure
Health assessment
• Health history taking
• Perform assessment: General
Body systems
• Use various methods of
physical examination
• Inspection, Palpation,
Percussion, Auscultation,
Olfaction Identication of
system
• wise deviations
Prepare Patient’s unit:
• Prepare beds:
• Open, closed, occupied,
operation, amputation,
• Cardiac, fracture, burn,
Divided, & Fowler’s bed
• Pain assessment and
provision for comfort
Use comfort devices Hygienic
care:
• Oral hygiene:
• Baths and care of pressure
points
• Hair wash, Pediculosis
treatment
• Write nurses
notes and
present the
patient report
of 2-3 assigned
patients
• Lab practice
• Measure
Vital signs
of assigned
patient
• Practice in lab
& hospital
• Assessment of
performance
with rating
scale
• Assessment of
each skill with
checklist
• Completion of
activity record
56
Areas Time
(Hours)
Objectives Skills Assignments Assessment
methods
Feeding:
• Oral/ Enteral,Naso/Orogastric,
gastrostomy and Parenteral
feeding
• Naso-gastric tube insertion,
suction, and irrigation
Assisting patient in urinary
elimination
• Provide urinal/bed pan
• Condom drainage
• Perineal care
• Catheterization
• Care of urinary drainage
Bladder irrigation Assisting
bowel Elimination:
• Insertion of Flatus tube
• Enemas
• Insertion of Suppository
Bowel wash Body Alignment
and Mobility:
• Range of motion exercises
•
Positioning: Recumbent,
Lateral, Fowlers, Sims,
Lithotomy, Prone,
Trendelenburg positon-
•
Assist patient in Moving,
lifting, transferring, walking
•
Restraints
Oxygen administration
• Mask
•
Prongs
•
Tent
• Catheters
Suctioning: oropharyngeal,
nasopharyngeal
Chest physiotherapy and
postural drainage
Care of Chest drainage
CPR- Basic life support
Observation of Intravenous
therapy
•
Simulated
exercise
on CPR
manikin
57
Areas Time
(Hours)
Objectives Skills Assignments Assessment
methods
• Performs
infection
control
procedures
Blood and blood component
therapy
Collect/assist for collection of
specimens for investigations
Urine, sputum, faeces,
vomitus, blood and other
body uids
Perform lab tests:
•
Urine: sugar, albumin,
acetone
• Blood: sugar (with strip/
gluco-meter)
Application of hot and cold
therapies:
• Local and general
• Dry and moist
Communicating and assisting
with self-care of visually &
hearing impaired patients
Communicating and assisting
with self-care of mentally
challenged/disturbed patients
Recreational and diversional
therapies
Caring of patient with
alteration in sensorium
Infection control
• Perform following
procedures:
• Hand washing techniques
• Simple, hand antisepsis and
surgical antisepsis (scrub)
• Prepare isolation unit in lab/
ward
•
Observation
study -2
•
Department
of Infection
control &
CSSD
•
Visits
CSSD write
observation
report 1
• Assess
observation
study with
checklist
•
Evaluate all
procedures
with
checklist
58
Areas Time
(Hours)
Objectives Skills Assignments Assessment
methods
• Provide
care to pre
and post-
operative
patients
• Perform
procedures
for care of
wounds
Administers
drugs
• Practice technique of
wearing and removing
Personal protective
equipment (PPE)
• Practice Standard safety
precautions (Universal
precautions)
Decontamination of
equipment and unit:
• Surgical asepsis:
• Sterilization
• Handling sterilized
equipment
• Calculate strengths of
solutions,
• Prepare solutions
• Care of articles
Pre and post-operative care:
• Skin preparations for
surgery: Local
• Preparation of Post-
operative unit
• Pre & post- operative
teaching and counselling.
• Pre and post-operative
monitoring
• Care of the wound:
• Dressings of minor
wounds, careof Drainage /
Application of Binders,
Splints& Slings
• Bandaging of various body
parts
Administration of
medications
• Administer Medications in
different forms and routes
• Oral, Sublingual and Buccal
• Parenteral : Intradermal,
subcutaneous, Intramuscular
etc.
• Assist with Intravenous
medications
• Collection of
samples for
culture
• Do clinical
posting in
infection
control
department
and write
report
• Practice in
lab/ward

59
• Provide
care to
dying and
dead
• Counsel
and support
relatives
• Drug measurements and
dose calculations
• Preparation of lotions and
solutions
• Administer topical
applications
• Insertion of drug into body
cavity: Suppository &
medicated packing etc.
• Instillation of medicines
into Ear, Eye, Nose and
throat
• Irrigations: Eye, Ear,
bladder, Vagina and Rectum
• Inhalations: dry and moist
• Medicated/Nebulization
• Identication of spurious
drugs.
• Record date, time,
medication, dose, route
And sign immediately after
administration
Care of dying patient
• Provide care for the
terminally ill
• Caring and packing of dead
Body
• Counseling and supporting
grieving relatives
• Handing over the body &
valuables
• Transferring to mortuary
with proper identication
• Terminal care of the unit
60
Placement- FIRST YEAR Time- 180 hours
CHN-I – 80 hours
Environmental Hygiene- 30 hours
Health Education & Communication skills- 40 hours
Nutrition- 30hours
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING – I
Course Description
This course is designed to help students gain an understanding of the concept of community health in order to
introduce them to the wider horizons of rendering nursing services in a community set – up, both in urban and
rural areas.
General Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the students shall be able to:
1 Describe the concept of health, community health and community health nursing.
2 State the principles of epidemiology and epidemiological methods in community health nursing practice.
3 Explain the various services provided to the community and role of the nurse.
4 Demonstrate skills to practice effective nursing care of the individuals and families in the clinics as well
as in their homes, using scientic principles.
Total Hours – 80
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr
Teaching
Learning
activities
Method of
Assessment
I Describe the concept of
health and disease and
community health
Introduction to Community Health
a) Denitions: Community,
Community health, community
health nursing
b) Concept of Health and disease,
dimensions and indicators of health,
Health determinants
c) History & development of
Community Health in India& its
present concept.
d) Primary health care, Millennium
Development Goals
e) Promotion and maintenance of
Health
10 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short Answers
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
61
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr
Teaching
Learning
activities
Method of
Assessment
II Explain various aspects
of Community Health
Nursing. Demonstrate
skills in applying
nursing process in
Community Health
Nursing settings
Community Health Nursing
a) Philosophy, goals, objectives &
principles , concept and importance
of Community Health Nursing,
b) Qualities and functions of
Community Health Nurse
c) Steps of nursing process;
community identication,
population composition, health
and allied resources, community
assessment, planning & conducting
community nursing care services.
14 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short answers
Essay type
III Demonstrate skill in
assessing the health
status and identify
deviations from normal
parameters in different
age groups.
Health Assessment
a) Characteristics of a healthy
individual
b) Health assessment of infant,
preschool, school going, adolescent,
adult, antenatal woman, postnatal
woman, and elderly.
10 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Role Play
Videos
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
IV Describe the principles
of epidemiology
and epidemiological
methods in community
health nursing practice.
Principles of Epidemiology and
Epidemiological methods
a) Denition and aims of
epidemiology, communicable and
non-communicable diseases.
b) Basic tools of measurement in
epidemiology
c) Uses of epidemiology
d) Disease cycle
e) Spectrum of disease
f) Levels of prevention of disease.
g) Disease transmission – direct and
indirect.
h) Immunizing agents, immunization
and national immunization
schedule.
i) Control of infectious diseases.
j) Disinfection.
10 Lecture cum
discussions.
Non-
communicable
disease module
of government
of India.
Field visit
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
V Demonstrate
skill in providing
comprehensive nursing
care to the family.
Family Health Nursing Care
a) Family as a unit of health
b) Concept, goals, objectives
c) Family health care services
d) Family health care plan and nursing
process.
12 Lecture cum
discussions.
Role play
Family visit
Short answers
Essay type
62
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr
Teaching
Learning
activities
Method of
Assessment
e) Family health services – Maternal,
child care and family welfare
services.
f) Roles and function of a community
health nurse in family health
service.
g) Family health records.
VI. Describe the principles
and techniques of family
health care services at
home and in clinics.
Family Health Care Settings Home
Visit:
a) Purposes, Principles
b) Planning and evaluation
c) Bag technique
d) Clinic: Purposes, type of clinics and
their functions
e) Function of Health personnel in
clinics
10 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Visits – Home,
health center
Short answer
Return
demonstration
VII Describe the referral
system and community
resources for referral
Referral System
a) Levels of health care and health care
settings.
b) Referral services available
c) Steps in referral.
d) Role of a nurse in referral
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Mock drill
Short answer
Objective type
VIII List the records
and reports used in
community health
nursing practice
Records and reports
a) Types and uses
b) Essential requirements of records
and reports
c) Preparation & Maintenance
3 Lecture cum
discussions.
Exhibit the
records.
Short answer
Objective type
IX. Explain the management
of minor ailments.
Minor Ailments
a) Principles of management
b) Management as per standing
instructions/orders.
5 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short answer
Objective type
63
Areas Duration Objectives Skills Assignments
Assessment
methods
Community
health
Nursing -
urban / rural
8 weeks a) Organize home visit
b) Prepare bagand
demonstrate bag
technique.
c) Build up and maintain
rapport with family.
d) Identify needs of
community
e) Practice procedure
f) Make referrals.
g) Plan and conduct health
education on identied
health needs.
h) Set up clinics with help
of staff.
i) Maintain records and
reports
j) Collect and record vital
health statistics.
k) Learn about various
organizations of
community health
importance.
l) Health Assessment
family
m) Identify the health needs
of various age groups.
n) Assess the environment
o) Maintain family folders.
p) Assessment nutritional
needs
q) Demonstrate different
method of preparing
food according to the
nutritional need of
family.
• Conducting Home
visits.
• Nutritional
assessment of
individuals.
• Provide care
at home as per
Standing Orders /
protocol.
• Conduct health
Education.
• Set up of different
Clinics.
• Maintain Records
& Reports.
• Practice family
health nursing.
• Demonstrate
different methods
of preparation of
Meals.
• Daily Diary
• Health
talk -2
• Family care
plan based
on family
study -2.
• Health
assessment
of an
individual -2
• Community
Prole – 2
• Report of
visit to water
purication
plant,
sewage
plant,
milk dairy,
panchayat.
• Assess
clinical
performance
with rating
scale.
• Evaluation of
daily diary,
health talk,
family care
plan, health
assessment,
community
prole,
observation
report.
Placement: FIRST YEAR Time: Practical – 320 hours (8 weeks)
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING I- PRACTICAL
64
ENVIRONMENTAL HYGIENE
Course Description
This course is designed to help students acquire the concept of health, understanding of the principles of
environmental health and its relation to nursing in health and disease.
General Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the students shall be able to:
1 Describe the concept and principles of environmental health.
2 Demonstrate skills to apply the principles of environmental hygiene in caring for self and others.
3 Describe the environmental health hazards, related health problems and the services available to meet
them.
Total Hours – 30
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Unit wise Hr
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
assessment
I Explain the
importance
of healthy
environment
and its relation
to health and
disease.
Introduction
a) Components of environment
b) Importance of healthy environment
2 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short answer
II Describe the
environmental
factors
contributing to
health andillness.
Environmental Factors Contributing to
Health
a) Water :
- Sources and characteristics of safe and
wholesome water
- Uses of water.
- Rain water harvesting
- Water pollution – natural and acquired
impurities
- Water borne diseases
- Water purication-small and large scale
b) Air :
- Composition of air
- Airborne diseases
- Air pollution and its effect on health
- Control of air pollution and use of safety
measures.
22 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstration
Exhibits
Visit to water
Purication
plant, sewage
treatment plant
Short
answers
Objective
type
Essay type
65
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Unit wise Hr
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
assessment
c) Waste :
- Refuse – garbage, excreta and sewage
- Health hazards
- Waste management: collection,
transportation and disposal.
d) Housing:
- Location
- Type
- Characteristics of good housing
- Basic amenities
- Town planning
e) Ventilation:
- Types and standards of ventilation
f) Lighting:
- Requirements of good lighting
- Natural and articial lighting
- Use of solar energy
g) Noise
- Sources of noise
- Community noise levels
- Effects of noise pollution
- Noise Control measures
h) Arthropods:
- Mosquitoes, housey, sand y, human
louse, rat eas, rodents, ticks etc.
- Control measures
III. Describe the
community
organization
to promote
environmental
health.
Community organizations to promote
environmental health
a) Levels and types of agencies:
- National, state, local
- Government, voluntary and social
agencies.
b) Legislations and acts regulating the
environmental hygiene.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short answer
Objective
type.
66
HEALTH EDUCATION AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS
Course Description
This course is designed to help students to
1. Acquire the concept of health education and develop an ability to select and/or prepare appropriate
audio-visual aids and use them effectively to communicate with the individuals and community
2. Understand the principles of communication and counseling, and its application in nursing practice.
General Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the students shall be able to:
1 Describe the concept of health education, communication skills including soft skills, audio – visual
aids and health education agencies.
2 Identify and utilize opportunities for health education.
3 Describe the application of information technology in preparation and use of various health teaching
aids.
4 Develop effective communication and counseling skills.
Total Hours – 40
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
I Describe the
concept and
different aspects
of communica-
tion
Communication Skills
a) Denition, process, purposes, principles,
types and importance of communication
b) Barriers in communication
c) Establishment of successful
communication.
d) Observing and listening skills.
8 Lecture cum
discussions.
Demonstration
Role play
Short answers
Objective type
Return
demonstration
II Describe the
aims and
objectives,
scope, levels,
approaches and
principles of
health education
Health Education
a) Concept, denition, aims and objectives
of health education
b) Principles of health education
c) Process of change/modication of health
behavior
d) Levels and approaches of health
education
e) Methods of health education
f) Scope and opportunities for health
education in hospital and community
g) Nurse’s role in health education.
6 Lecture cum
discussions.
Short answers
Objective type
67
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
III Demonstrate
the skills of
counseling.
Counseling
a) Denition, purpose, principles, scope and
types
b) Counseling process: steps and techniques
c) Qualities of a good counselor
d) Difference between health education and
counseling
e) Role of nurse in counseling
8 Lecture cum
discussion
Role play
Short answer
Essay type.
IV Describe the
types of AV
aids.
Demonstrate
skill in
preparing and
using different
kinds of audio –
visual aids
Methods and Media of Health Education
a) Denition, purpose and types of audio-
visual aids and media
b) Selection, preparation and use of audio-
visual aids : graphic aids, printed aids,
three dimensional aids and projected aids
c) Advantages and limitations of different
media
d) Preparation of health education plan
18 Lecture cum
discussions
Exhibits.
Demonstration
Evaluation of
prepared audio
visual aids.
Written test
68
NUTRITION
Course Description
This course is designed to help students understand that nutrition is an integral component of health as
nutrients play a vital role in the growth, development and maintenance of the body.
General Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the students shall be able to:
1 Describe the principles of nutrition and dietetics and its relationship to the human body in health and
disease.
2 Describe the balanced diet in promotion of health
3 Apply this knowledge in providing therapeutic diet in care of the sick.
4 Demonstrate skills in selection, preparation and preservation of food.
Total Hours – 30
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Methods of
assessment
I
Describe the
relationship
between nutrition
and health
Introduction
a) Meaning of food, nutrition,
nutrients etc.
b) Food Habits and customs
c) Factors affecting nutrition
d) Changing concepts in food and
nutrition.
e) Relation of Nutrition to Health
2
Lecture cum
discussions.
Explain using
charts
Short answer
types
Objective type
II
Describe the
classication of
food.
Classication of food
a) Classication by origin:
- Food and animal origin
- Food of plant origin
b) Classication by chemical
composition and sources
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Minerals
- Vitamins
- Water
c) Classication by predominant
functions
- Body building food
- Energy giving food
- Protective food
2
Lecture cum
discussions.
Real food
items
Exhibits charts
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
69
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Methods of
assessment
d) Classication by nutritive value
- Cereals and millets
- Pulses and legumes
- Vegetables
- Nuts and oil seeds
- Fruits
- Animal food
- Fats and oils
- Sugar and jiggery
- Condiments and spices
- Miscellaneous food.
III Explain
normal dietary
requirements
Demonstrate skill
in calculating
normal food
requirements.
Normal Dietary Requirements
a) Energy: Calorie, Measurement,
Body Mass Index, BasalMetabolic
Rate – determination and factors
affecting
b) Balanced Diet – nutritive value
of foods, calculation for different
categories of people, normal
food requirement calculation.
Menu plan. Combination of
food affecting and enhancing
the nutritive value of the diet.
c) Budgeting for food, low cost
meals, food substitutes.
d) Diseases and disorders caused by
the imbalance of nutrients.
e) Food allergy –causes, types, diet
modications in glutein, lactose
and protein intolerance etc.
f) Food intolerance - inborn errors of
metabolism
4 Lecture cum
discussions.
Charts exhibits
Real food
Practical
exercise
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
IV Describe
theprinciples and
various methods
of preparation,
preservation and
storage of food.
Food Preparation, Preservation &
Storage
a) Principles of cooking, methods of
cooking and the effect of cooking
on food and various nutrients.
Safe food handling, health of food
handlers.
2 Lecture cum
discussions.
Field visit
to food
processing
unit.
Short answer
type
Objective type
70
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Methods of
assessment
b) Methods of food preservation–
household and commercial,
precautions.
c) Food storage – cooked and raw,
household and commercial, ill
effects of poorly stored food.
d) Food adulteration and acts related
to it.
Demonstration
exhibits
Evaluation
of exhibit
preparation.
V Describe about
therapeutic diet
Therapeutic Diet
a) Diet modication in relation to
medical and surgical condition
of the individual such as Protein
Energy Malnutrition (PEM),
Diabetes, Cardio Vascular
disease, Hepatitis, Renal, Gouts,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS),
Obesity, cholecystectomy,
partial gastrectomy, gastrostomy,
bariatric surgery and colostomy
etc.
b) Special diet – low sodium diet, fat
free diet, diabetic diet, bland diet,
high protein diet, low protein diet,
low calorie diet, geriatric diet,iron
rich diet, liquid diet, semi-solid
diet, soft diet and high ber
dietetc
c) Factors affecting diet acceptance,
feeding the helpless patient.
d) Health education on nutrition
needs and methods in diet
modication .
8 Lecture cum
discussions.
Practical of
planning
Therapeutic
diet
Demonstration
Charts
Exhibits
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
VI Describe the
concept of
community
nutrition
Community Nutrition
a) Nutritional problems and
programs in India
b) Community food supply, food
hygiene and commercially
prepared and grown food available
locally.
c) National and international food
agencies – Central food training
research institute (CFTRI), Food
and agriculture organization
4 Lecture cum
discussions.
Videos
Government of
India nutrition
manuals.
Short answer
Objective type
71
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Methods of
assessment
(FAO), National Institute of
Nutrition (NIN), Food Safety
and Standards Authority of India
(FSSAI), CARE (Cooperative
for Assistance and Relief
Everywhere), National Institute
of Public Cooperation and Child
Development (NIPCCD) etc.
Visit to the
local food
preparation
/ processing
agency.
VII Demonstrate skill
in preparation of
common food
items.
Preparation of diet / practical
a) Beverages: hot and cold, juice,
shakes, soups, lassi, barley water
b) Egg preparation: egg ip,
scramble, omlet, poached egg
c) Light diet: porridges, gruel,
khichari, dahlia, kanji, boiled
vegetables, salads, custards.
d) Low cost high nutrition diets -
chikki, multigrain roti
8 Lecture cum
discussions
Cookery
practical
Practical
evaluation
72
Placement- FIRST YEAR Time- 30 hours
Course Description
This course is designed to help students develop an ability to comprehend spoken and written English, so as
to communicate effectively.
General Objectives
Upon completion of this course, the students shall be able to:
1 Read and write correct English.
2 Communicate effectively in English.
Total Hours-30
Unit
Learning
Objective
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Method
I. Speak and
write correct
grammatical
English
Grammar
a) Review of basic grammar
b) Building Vocabulary
6 Discussion,
written and oral
exercises.
Objective type
Paraphrasing
II Develop
ability to read ,
understand and
write in English
Composition
a) Sentence construction and usage.
b) Reading comprehension.
c) Written composition : paragraphs
& essays, precise writing, story
writing & comprehension, letter
writing, nurses notes and reports,
anecdotal records, diary writing
14 Discussion
Written and oral
exercises.
Dictation
Exercise
Objective type
Translation
Report
evaluation
Essay type
III Demonstrate
conversation
skills.
Spoken English
a) Conversation – face to face and
telephonic
b) Oral report
c) Discussion, debate
d) Public speaking skills.
10 Discussion,
written and oral
exercises.
Extempore
Debates
Discussion
ENGLISH
73
Placement- FIRST YEAR Time- 15 hours
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help students gain a basic understanding of uses of computers and its application in
nursing.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the basic disk operating system.
2. Use computer for data processing
3. Use Micro-soft ofce programs.
4. Use computer in patient Management System.
5. Use E-mail and internet
Total Hours – 15
Unit
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Describe the
structure and
purpose of
computers and
disc operating
systems
Introduction to computers and Disk
operating system
a) Denition
b) Classication
c) Structure and parts of computer
d) Disk operating system – DOS and
WINDOWS all versions.
e) Purposes / uses of computer is health
care delivery system
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Practical
Short answers
Essay type
Practical
II Demonstrate skill
in the use of MS
ofce
MS Ofce
a) MS word
b) MS excel with pictorial presentation
c) MS Power point
d) MS access
e) MS publisher document
15 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Practice session
Short answer
Objective type
Practical exam
III Demonstrateskill
in using
multimedia
Multimedia
a) Types and uses
b) Data base creation, retrieval and report
generation
c) Computer aided teaching and testing
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Practical exam
IV Demonstrate the
use of internet and
e-mail
Use of internet and e-mail
a) Accessing the website
b) Searching the internet for content
c) Accessing the email and communicating
with the help of it.
d) Use of internet communication programs
– skype
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Practical exam
COMPUTER EDUCATION
74
Placement- SECOND YEAR Time- 120 hours
Course Description:-
This course shall help students understand the concept of disease and disease process, Students shall be able
to gain knowledge and develop understanding of various medical, surgical disorders and disease. They shall
be able to give comprehensive nursing care to patient with these diseases.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the cause, symptoms, treatment and prevention of Medical Surgical Diseases.
2. Demonstrate skill in carrying out nursing technique and procedures with the applicant of scientic
principles.
3. Discuss nursing process and provide nursing care to patients with medical surgical/ diseases.
Total Hours - 120
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
I Explain the
history of modern
Medicine and
Surgery
Introduction
a) Brief history of evolution of modern
medicine and surgery
b) Theories of illness and its causation -Illness
as human experience
c) Review of Nursing process and Nursing care
plan.
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Objective type
II Demonstrate skill
in conducting
health assessment
and physical
examination
Nursing assessment
a) Health Assessment
- Health history
- Physical examination
- Nutritional assessment
- General clinical investigations
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Simulation
Short answer
Objective type
Return
demonstration
III Describe the
pathophysiolo-
gical mechanism of
diseases
Pathophysiological mechanism of disease
a) Stress adaptation stressors, management,
Nursing interventions
b) Inammation
c) Defense against injury
d) Nutritional consideration
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Topic presentation
Short answer
Essay type
IV Demonstrate skill in
providing nursing
care to patients with
altered immune
response.
Altered immune response
a) Overview of normal immune system
b) Altered immune response, hypersensitivity
and allergy
c) Assessment of immune system
d) Diagnostic evaluation
e) Allergy disorders:
- Anaphylaxis
- Allergic rhinitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis
6 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical case
presentation
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING- I
75
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
- Drug reactions
- Food allergy
- Serum sickness
- Latex allergy
f) Approaches to treatallergic diseases
g) Nursing management client with altered
immune response
h) Auto immune disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Graft versus host disease
V Demonstrate skill
in management of
client with uid
and electrolyte
imbalance.
Fluid and electrolyte balance and Imbalance
a) Water contents of body, electrolyte and Acid
– Base balance
b) Homeostasis
c) Review mechanism of regulating uid and
electrolyte movement
d) Fluid and electrolyte Acid-Base imbalance
and its management
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
VI Describe physical
set up of OT and
its equipments.
Demonstrate skill in
theatre techniques.
Operation theatre technique:
a) Physical Environment
- Operation theatre room - cleaning of tables,
trolleys, lights and other equipments
- Pre-operative holding areas.
b) Theatre Technique
- Scrubbing – Hand washing
- Gowning
- Gloving
- Positioning of patient for various surgical
procedures.
- Draping of patient.
c) Preparation of theatre, equipment and
supplies
- Cleaning
- Needles, sutures – types and their uses.
- Carbolization, ETO sterilization,
fumigation, OT swab, Bacillocid
sterilization.
- Packing and sterilization of dressings, linen
rubber ware suture material, instruments,
needlesandother materials.
8 Lecture cum
discussion
Explain about the
instruments
Demonstration
of OT techniques
– scrubbing,
gowning, gloving
Positioning and
draping
Visit to CSSD
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
VII Demonstrate skill in
preparing the client
for surgery.
Recognize and
perform the role
of nurse during
surgery.
Management of patient undergoing surgery
a) Pre operative preparation and care
- Physical
- Psychological,
- Pre-medications
- Legal and ethical
b) Intra operative management
- Surgical Team
- Nursing activities and responsibilities
- Anesthetic agents
- Role of nurse in anesthesia
8 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Videos
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
76
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
Demonstrate skill
in giving care to
clients after surgery
(post-operative
care)
c) Post operative Management
- Immediate care
- Transferring patient from operation theatre
- Patient in recovery room
- Recovery from Anesthesia
- Post operative observation and nursing
management
- Carryout the post operative orders.
- Postoperative complication observation,
prevention & management.
VIII Demonstrate skills
in the nursing
management of
client with impaired
respiratory function
and gaseous
exchange
Nursing management of patient with impaired
respiratory function and gaseous exchange
a) Assessment of respiratory function
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic evaluation
b) Care of patient in respiratory intensive care
and ventilator care and respiratory function
c) Management of Patient with disorders of
upper respiratory airway.
- Obstruction of upper airway
- Epistaxis
- Sinusitis
- Pharyngitis
- Tonsillitis
- Laryngitis
- Deviated nasal septum
d) Management of patient with disorders of the
chest and lower respiratory tract
e) Management of patient with impaired • Lung
abscess
- Empyema
- Bronchial asthma
- COPD
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Bronchiectasis
- Trauma
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis/DOTS
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary edema
- Lung tumors
- Disorders of pleura and pleural space
- Lung surgery
- Respiratory failure
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome,
- SARS
f) Alternate therapies
g) Drugs used in treatment of disorder of
respiratory system
15 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration of
various articial
respiratory devices
Simulation
Case discussion
Videos and Films
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
77
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
IX Describe the
various gastro
intestinal disorders.
Demonstrate skill in
providing care for
clients with gastro
intestinal disorders.
Nursing management of patient with gastro
intestinal disorders
a) Assessment of gastro intestinal function
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic evaluation
b) Management of Upper gastrointestinal
disorders
- Parotitis
- Stomatitis
- Glossitis
- Gingivitis
- Pyorrhea
- Dental caries
- Halitosis
- Dysphagia
- Achalasiacardia
- Gastro Esophageal Reux Disease (GERD)
- Cancer of esophagus
- Hiatus hernia
- Gastritis
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers
- Gastric cancer
- Gastroenteritis
- Esophageal stula
- Peritonitis
c) Care of patient with gastro intestinal
intubation and special nutritional
management.
d) Management of patient with lower gastro
intestinal disorders:
- Helminthiasis
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Fecal incontinence
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Appendicitis
- Diverticular disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Intestinal obstruction
- Colitis
- TB abdomen
- Colorectal cancer
- Polyps of colon and rectum
- Ano rectal abscess
- Anal stula and ssure
- Hemorrhoids
e) Alternate therapies
f) Drugs used in treatment of GI disorders
18 Lecture cum
discussion
Visit to endoscopy
room, radiology
department
Demonstration
Films and Videos
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
78
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
X Describe the
management
of patients
with metabolic
and endocrinal
disorders.
Demonstrate
skills in caring
for the clients
with metabolic
and endocrinal
disorders.
Nursing management of patients with
metabolic and endocrinal disorders:
a) Assessment of Hepatic and biliary functions
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic measures
b) Management of patients with hepatic
disorders
- Jaundice
- Hepatic cirrhosis
- Portal hypertension
- Ascites
- Hepatic Encephalopathy and coma
- Viral hepatitis
- Tumors and cyst of the liver
- Liver abscess
c) Management of patients with biliary
disorders
- Cholecystitis
- Cholelithiasis
- Choledocolithiasis
- Acute and chronic pancreatitis
- Cancer of pancreas
d) Assessment of Endocrinal function
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic evaluation
c) Management of endocrinal disorders
- Pituitary disorders
- Thyroid disorders
• Hyperthyroidism
• Hypothyroidism
• Thyroid tumors
• Goiter
- Parathyroid disorders
- Pancreas disorder
• Diabetes mellitus
- Adrenal disorders
• Pheochromocytoma
• Addison’s disease
• Cushing’s syndrome
- Tumors of the endocrine glands
f) Alternate therapies
g) Drugs used in treatment of metabolic and
Endocrine disorder
15 Lecture cum
discussion
Charts
Simulation
Clinical teaching
Exposure to
diagnostic
procedures
Videos and Films
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
XI Describe the
management of
clients with urinary
and renal disorders.
Demonstrate skill in
giving care of client
with urinary and
renal disorders
Nursing management of renal and urinary
disorders
a) Assessment of renal and urinary functions
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic evaluation
b) Management of patients with renal and
urinary disorders
- Urinary retention and incontinence
- Urinary tract infection
14 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Visit to Dialysis
unit
Videos and Films
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
79
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
. - Acute and chronic glomerulonephritis
- Pyelonephritis
- Urolithiasis
- Renal calculi
- Trauma of kidney, bladder,urethra, ureters
- Urinary strictures
- TB of urinary tract
- Neurogenic bladder dysfunction
- Renal cyst and renal abscess
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Acute and chronic Renal failure
- Uremia
- Acute and chronic nephrosis
- Tumor – benign and malignant
- Care of patient on hemodialysis and
peritoneal dialysis
- Care of patient with renal transplant
c) Assessment of male Genitourinary function
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic evaluation
d) Disorders of male genito urinary tract and its
management
- Hydrocele,
- Phimosis
- Benign and malignant prostatic
hypertrophy
- Orchitis
- Epididymoorchitis
- Cancer penis
e) Alternate therapies
f) Drugs used in treatment of renal and Urinary
disorders
XII Describe
the nursing
management
of clients with
Neurological
disorders
Nursing management of patients with
neurological disorders:
a) Assessment Neurological functions
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic evaluation
b) Management of patients with neurologic
dysfunctions
- Altered level of consciousness
- Increased Intracranial pressure
- Intracranial surgery
c) Management of patients with neurological
disorders
- Headache
- Migraine
- Seizures
- Epilepsy
- Status epileptics
- Cerebrovascular disorder – CVA
- Neurological trauma – Head, brain, spinal
cord, subdural and extradural hematoma
- Neurologic infection
• Meningitis
20 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Demonstration of
reexes and use
of Glasgow coma
scale
Simulation
Videos and Films
Charts
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
80
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
Methods
Demonstrate skill
in giving nursing
care to clients
with Neurological
disorders
• Brain abscess
• Encephalitis
- Degenerative disorders
• Multiple sclerosis
• Myasthenia gravis
• Guillain – Barre syndrome
• Parkinsonism
• Alzheimer disease
- Neuralgia
- Bell’s Palsy
- Peripheral neuropathies
- Brain and spinal cord tumors
- Huntington’s disease
- Muscular Dystrophies
- Herniation of the intervertebral disc
d) Alternate therapies
e) Drugs used in treatment of neurological
disorders
XIII Describe the
management
of clients with
connective tissue
and collagen
disorders
Demonstrate skill in
providing nursing
care to clients
with connective
tissue and collagen
disorders
Nursing Management of Patients with
Connective Tissue and Collagen Disorders
a) Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic measures
b) Management of patients with disorders of
connective tissue and collagen disorders
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Scleroderma
- Polymyositis
- Osteoarthritis
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Gout
- Fibromyalgia
c) Alternate therapies
d) Drugs used in treatment of connective tissue
and collagen disorders
8 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
XIV Describe the nurse’s
role in promoting
wellness for elderly.
Demonstrate skill in
providing nursing
care for elderly
clients.
Nursing management of the elderly
a) Assessment of the elderly
- Ageing process
- Helping and care of elderly in promoting
wellness and self care
b) Conditions associated with ageing
- Dementia
- Osteoporosis
- Incontinence – urinary
- Sensory deprivation
c) Home and Institutional care
6 Lecture cum
discussion
Visit to old age
home
Videos
Short answer
Objective type
81
Placement- SECOND YEAR Time- 120 hours
Course Description:-
This course shall help students understand the concept of disease and disease process, Students shall be able
to gain knowledge and develop understanding of various medical surgical specialty disorders and disease.
They shall be able to give comprehensive nursing care to patient with these diseases.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the cause, symptoms, signs, treatment and prevention of diseases classied under medical
Surgical Specialties.
2. Demonstrate skill in carrying out nursing technique and procedures with the applicant of scientic
principles.
3. Prepare nursing care plan using nursing process and apply it in provide care to patient with these
diseases.
Total Hours - 120
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
I
Describe the
management of
patients with
oncology
Oncology Nursing:
a) Nursing management of patients with
oncological conditions
- Structure & characteristics of normal &
cancer cells
- Nursing Assessment-History and Physical
assessment
- Prevention, Screening, Early detection,
Warning signs of cancer
- Epidemiology, Etiology, Classication,
Pathopysiology, staging, clinical
manifestations, diagnosis, treatment
modalities and medical & surgical nursing
management of oncological conditions
- Common malignanacies of various body
systems: Oral, larynx, lung, stomach and
Colon, Liver, Leukemias and lymphomas,
Breast, Cervix, Ovary, uterus, Sarcoma,
Brain, Renal, Bladder, Prostate etc
b) Oncological emergiences
c) Modalities of treatment
- Immunotherapy
15
Lecture cum
discussion
Explain using
charts, graphs
models, lms,
and slides
Case discussion
Seminar
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING- II
82
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
- Radiotherapy
- Surgical Interventions
- Stem cell and Bonemarrow transplants
- Gene therapy
- Other forms of treatment
d) Psychosocial aspects of cancer
e) Rehabilitation
f) Palliative care: symptom and pain
management, Nutritional support
g) Home care
h) Hospice care
i) Stomal Therapy
j) Special therapies
k) Psycho social aspects
l) Nursing procedures
m) Alternate therapies
n) Drugs used in treatment of oncological
disorders
Drug book
Lecture cum
discussion
Topic
presentation
Posting to
cancer Hospital/
unit
Structured
discussion
Seminar
Assessment
of skills with
check list
II Describe the
disorders of
breast and breast
cancer.
Demonstrate skill
in giving nursing
care to patients
with breast
disorders
Nursing Management of patients with
disorders of Breast
a) Assessment of breast
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic tests
- Breast self examination
b) Disorders of breast
- Mastitis
- Breast abscess
- Gynaecomastia
- Tumors and Malignancy of breast
c) Nursing management of a patient after
mastectomy.
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Models and
exhibits
Short answer
Objective type
Essay
III Describe the
various diseases
and disorders of
integumentary
system and their
management.
Demonstrate
skill in providing
care to the clients
with disorders
of integumentry
system
Nursing Management of patient with
diseases and disorders of integumentary
system
a) Nursing Assessment
- History
- Physical assessment
b) Etiology
c) Pathophysiology
d) Clinical manifestions
e) Nursing management of disorders of skin
and its appendages
- Lesions and abrasions
- Infection and infestations Dermititis
- Dermatoses; infectious and Non
infectious
- Inammatory dermatoses
- Acne Vulgaris
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Explain using
Charts, graphs
models, lms,
slides
Essay type
Short answers
Object type
Assessment
of skills with
check list
83
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
- Allergies and Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Malignant Melanoma
- Alopecia
- Infestations
- Bacterial infections
- Pyoderma
- Impetigo
- Folliculitis
- Furuncles
- Carbuncles
- Viral infections
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Fungal infection
- Athlete’s foot (Tanta Pedi’s)
- Parasitic infestation
- Pediculosis
- Scabies
- Pemphigus
- Stevens - Johnson syndrome
- Skin cancer
- Special dermatological therapies
f) Burn and its management
- Burns Plastic Surgery
- Incidence, causes of burns
- Types & classication of burns
- Pathophysiology
- Calculation of the percentage
- Local & systematic effects of burns
- Immediate care
- First aid care
- Medical Management, barrier nursing
care of the burns
- Complications, Health education
g) Plastic Surgery
- Dene plastic & reconstructive surgery
- Types
- Dene skin graft aps
- Possible complication
- Preparation of patient for constructive
surgery
- Post operative care
- Health Education
h) Alternate therapies
i) Drugs used in treatment of integumentary
disorders
84
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
IV Describe the
disorder and
diseases of eye
Demonstrate
skill in giving
care for patients
with various
eye diseases and
disorders.
Ophthalmology And Ophthalmic Nursing
a) Review of anatomy and physiology of eye
b) Assessment of function of eyes.
- History
- Physical exam
- Diagnostic tests-tonometry, Snellen’s chart
c) Infections and Inammations conditions
- Blepharitis
- Stye
- Chalazion
- Entropion
- Ectopion
- Dacrocystitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Trachoma
- Pterydium
- Keratitis
- Corneal ulcer
d) Degenerative Conditions
- Cataract
- Retinopathy
- Retinal detachment
e) Miscellaneous
- Strabismus
- Refractive errors
- Tumors
- Color blindness
- Nigh Blindness
- Total blindness
f) Preventive and Rehabilitative aspects
g) National programs on Blindness and trachoma
h) Current trends in Management of Ophthalmic
conditions
- Hospital corneal retrieval
- Grief counseling.
- Eye Collection
- Counselling
- Obtaining consent for eye donation
i) Eye banking in India
j) Ocular Emergencies
- Glaucoma
- Foreign body
- Acid / Alkali burns
- Trauma to the eye
k) Eye Immigration
l) Instillation of eye drops and ointment
m) Cold and hot compress
n) Eye dressing and bandage
o) Assisting for sac syringing
p) Assisting for removal of foreign body
q) Alternate therapies
r) Drugs used in treatment of eye disorders
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Visit school for
the blind
Visit to eye bank
Visit
National
Association for
the blind
Eye bank
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay
Return
demonstration
85
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
V Describe disorders
and diseases of ear,
nose and throat.
Demonstrate
skills in Providing
nursing care
for patients with
various ENT
problems.
Nursing Management of Patient with
Disorders and Diseases of Ear, Nose and
Throat
Ear
a) Review of Anatomy and physiology of Ear
b) Assessment of function of ear
- History
- Ear examination
- Diagnostic tests
c) Diseases and disorders of the ear
Externalear
- Otitis
- Foreign body
- Impacted cerement
- Furunculosis
Middleear
- Otitis media
- Mastoiditis
- Perforation of ear drum
Internalear
- Presycusis
- Labryinthitis
- Meniere’s disease
- Otosclerosis
Deafness
- Conductive deafness
- Neural deafness
Tumorsoftheearandauditorynerve
InsufationsofEustachiantube
Nose
a) Review of Anatomy and physiology of nose
b) Assessment of functions of nose
- History
- Examination of nose
- Diagnostic tests
c) Diseases and disorders of nose
Infections
- Rhinitis
- Sinusitis
- Obstruction
- Polyps
Foreignbody
Deviatednasalseptum
Trauma–fractureofnasalboneand
epitaxies
Throat
a) Review of Anatomy and physiology of Throat
15 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Demonstration
Videos, charts
Short answer
Objective type
Essay
Return
demonstration
86
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
b) Assessment of the function of throat
- History
- Examination of throat
- Diagnostic tests
c) Diseases and disorders of throat infections
and inammation
- Tonsillitis
- Pharyngitis
- Adenoiditis
- Laryngitis
- Tumors
- Injury and foreign body
- Alternate therapies
- Drugs used in treatment of ENT disorders
VI Describe
cardiovascular
circulatory and
Hematological
disorders and
diseases.
Demonstrates
skill in carrying
nursing
interventions
for clients with
circulatory and
hematological
disorders and
diseases.
Nursing Management of Patient with cardio
vascular, circulatory and Hematological
disorders
Cardio Vascular
a) Review of anatomy and physiology of heart
and circulatory system
b) Assessment of functions of heart and
vascular system
- History
- Physical exam
- Diagnostic tests
c) Diseases and disorders of cardio vascular
system
- Coronary Artery disease
- Arrhythmia
- Coronary Artery disease
• Angina pectoris
• Coronary atherosclerosis
• Myocardial infarction
- Valvular heart disease
• Mitral stenosis
• Aortic stenosis,
• Incompetence, regurgitation
• Tricuspid stenosis
• Pulmonary stenosis
- Inammation and infections
• Pericarditis, Myocarditis, Endocarditis
• Rheumatic fever
- Heart block
- Complication of heart disease
• Acute Heart failure (Pulmonary Edema)
• Chronic (Congestive Cardiac failure)
• Cardiogenic shock
87
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
• Pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade
- Cardiac emergencies
• Cardiac arrest
• Shock
- Vascular disorders
• Arterial disorders
• Berger’s disease (TAO),
• Arterial ulcers,
• Arteriosclerosis,
• Aneurysm,
• Thrombosis and emboli,
• Raynaud’s disease
• Hypertension
- Venous disorder
• Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
• Venous insufciency
• Venous ulcer
• Varicose vein
• Cellulitis
• Lymphatic disorders
• Lymphangitis & Lymphadenitis
• Lymphedema & elephantiasis
Hematological disorders
a) Review of function and structure of blood
components
- Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic tests
b) Diseases and disorders of blood and its
components
- Anemia
- Thalassemia
- Polycythemia
- Leukopenia and neutropenia
- Leukocytosis & leukemia
- Lymphomas Hodgkin & Non Hodgkin
diseases, Multiple myeloma
- Bleeding disorders
- Thrombocytopenia,
- Purpura, hemophilia
- Acquired coagulation
- Disorders – Liver disease, Vitamin K
deciency, DIC
c) Alternate therapies
d) Drugs used in treatment of cardiovascular
circulatory and hematology disorders
28 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Clinical
teaching
Videos,
Simulation
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
88
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
VII Describe
the nursing
management of
patients with
communicable
diseases.
Demonstrate
skill in providing
interventions
for patients with
communicable
the nurse’s
role in various
national control/
Eradication
Programme of
communicable
diseases.
Nursing Management of Patients with
communicable diseases
a) Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic tests
b) Review of infection, mode of transmission,
its prevention and control
c) Preparation, care and administration of anti
sera and vaccinesIsolation,
d) Management of various infection diseases
causedbyVirus;
- Measles
- Chicken pox
- Swine u
- Ebola
- Dengue
- Chicken guinea
- Inuenza
- Mumps
- Encephalitis
- Infective hepatitis
- Poliomyelitis
- Rabies
- AIDS
CausedbyBacteria;
- Diphtheria
- Whooping cough
- Tetanus
- Typhoid
- Dysentery
- Gastroenteritis
- Cholera
- Meningococcal Meningitis
- Tuberculosis
- Plague
- Leptospirosis
Vectorbornediseases;
- Malaria
- Filariasis
- Yellow fever
- Dengue
- Any other prevailing diseases
e) Alternate therapies
f) Drugs used in treatment of communicable
disorders
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Role play
Participate in
immunization
campaign
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Assesment
with clinical
checklist
89
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
VIII Describe
various sexually
transmitted
diseases.
Demonstrates
skills in
syndromic
management
of sexually
transmitted
diseases.
Nursing Management of Patients with
Sexually Transmitted deiseases
a) Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic tests
b) Sex health and hygiene
c) Syndromic Management of sexually
transmitted disease
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Granuloma Venerium
- Chanchroid granuloma
- AIDS
- Genital herpes
05 Lecture cum
discussion
Video
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
IX Describe various
musculo skeletal
disorders and
diseases.
Demonstrate
skills in
management of
musculo skeletal
diseases.
Nursing Management of Patients with
musculo skeletal disorders and diseases
a) Review of Anatomy and Physiology of
musculo skeletal system
b) Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Diagnostic tests
c) Infections and inammations
- Septic arthritis
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Osteomyelitis
- Tuberculosis of the spine and bones
- Sprains
- Dislocations
- Fracture of spine and extremities
d) Degenerative conditions of joints, spine
e) Tumors, Amputation and prosthesis
f) Deformities - Congenital and acquired
g) Range of motion exercises
h) Care of patient:
- Skin and skeletal traction
- Orthopedic splints
i) POP application and removal
j) Neurogenic bladder
k) Preparation for bone surgery
l) Use of orthopedic assist devices
- Crutches
- Canes
- Walker
m) Alternate therapies
n) Drugs used in treatment of musculo-skeletal
disorders disorders
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical
teaching
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
90
Unit
No.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Method of
Teaching
Assessment
methods
X Describe the
role of nurse in
medical surgical
emergencies
Demonstrate
skill in meeting
medical surgical
emergencies.
Emergency Management
a) Scope and practice of emergency nursing
- Principles of emergency care
- Triage
b) Medical Surgical Emergencies
c) Airways obstruction
- Hemorrhage
- Shock, Anaphylactic reaction, Allergies
- Trauma – intra abdominal, crush injuries,
multiple injures fractures
- Poisoning
- Ingested poisoning
- Inhaled poisoning
- Food poisoning
- Injected poisons – Stinging insects
- Snake bites Chemical burns
- Environmental emergencies:
- Heat stroke
- Frost bite.
- Near drowning
- Hanging
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Preparing
emergency
trolley -
Demonstration
of CPR -
Debrillation
Videos & Films
Simulation
Roleplay
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
XI Identify the role
of nurses in
emergency and
disasters.
Demonstrate
beginning skill
in managing the
Emergencies and
disasters.
Emergency and Disaster Nursing
a) Natural calamities
- Flood
- Earthquake
- Volcanic eruptions
b) Man-made disaster
- Explosion
- War
- Fire
- Accidents
c) Emergency preparedness
d) Community resources available to meet
calamities
e) Nurses role in disaster management
05 Lecture cum
discussion
Role play
Mock drill
INC: Disaster
management
module:
Reaching out:
nursing care
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
91
Placement- SECOND YEAR Time: 800 hours (20 weeks)
General objectives:
Students are able to apply nursing process and provide comprehensive nursing care to the clients with various
medical and surgical conditions
Specic objectives; students are able to;
1. Comprehend the causes, signs and symptoms, treatment and prevention of various medical, surgical
conditions.
2. Apply the theoretical knowledge to appropriate clinical nursing practice.
3. Identify the problems and needs, prioritize them and provide comprehensive nursing care by applying
nursing process
4. Demonstrate skills in carrying out nursing techniques, procedures in keeping with scientic
principles.
5. Demonstrate skills in respective clinical specialty.
6. Interpret and carry out the pharmacological intervention,
7. Identify the deviation from normal in the diagnostic value.
8. Plan and participate in rehabilitation of patient and family.
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
General
medical
wards
(resp.,GI,
Endo.,
hemato,
neuro,
renal)
3 wks • Provide
nursing care
to adult
patients with
medical
disorders
- Assessment of patient
• Take history
• Perform general & specic
physical examination
• Identify alterations and
deviations
- Practice medical-surgical
asepsis-standard safety
measures.
- Administer medications
• Oral
• Sub-lingual
• Intra-dermal
• Subcutaneous
• Intramuscular
• Intravenous
- Intravenous therapy
• IV canulation
• Maintenance & monitoring
- Oxygen therapy-mask,
prongs & tent
Plan &
implement care
for assigned
patients
• Nursing care
plan 1
• Nursing case
study-1 or
presentation-1
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
check list
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING- PRACTICAL
92
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
• Counsel
and educate
patients and
family
- Nebulization
- Chest physiotherapy
- Naso-gastric feeding
- Assist in common diagnostic
procedures
- Perform/assist in therapeutic
procedures
- Transfusion of Blood & its
components
- Throat suctioning
- ET suctioning
- Collect specimens for
common
- investigations
- Maintain elimination
• Catheterization
- Educate & counsel patient
& family regarding specic
disease conditions.
• Drug study
presentation-1
• Maintain drug
book
• Maintain
practical
record book
• Evaluation
of case study
presentation
• Completion
of practical
record
General
surgical
wards
(GI and
Urinary)
3 weeks • Provide pre &
post-operative
nursing care
to adult
patients with
surgical
disorders
• Educate
& counsel
patients and
families
- Practice medical-surgical
asepsis-standard safety.
- Pre-operative preparation of
patient
- Post-operative care
• Receiving
• Assessment
• Monitoring
- Care of wounds and drainage
- Suture removal
- Ambulation & exercises
- Naso-gastric aspiration
- Care of chest drainage
- Ostomy care
• Gastrostomy
• Enterostomy
• Colostomy
- Transfusion of Blood & its
components
- practice universal
precautions
Plan &
implement care
for assigned
patients
• Nursing care
plan 1
• Nursing case
study-1 or
presentation-1
• Drug study
presentation-1
• Maintain drug
book
• Maintain
practical
record book
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
check list
• Evaluation
of case study
presentation
• Completion
of practical
record
Operation
theater
3 weeks • Identify
instrum-
ents used
in different
operations
Perform scrubbing, gowning,
gloving
- Identify instruments,
suturing materials for
common operations.
Disinfection, carbolization
sterilization & fumigation
- Assist as a
scrub nurse for
5 major and 5
minor cases.
Assess skill
with check list
93
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
• Set-up the
table/ trolleys
for common
operative
procedures
• Assist in the
operative
procedu-res
• Provide peri-
operative
nursing care
- Prepare the OT table
depending upon the
operation
- Positioning and monitoring
of patient
- Assisting with minor &
major operations
- Handling specimens
- Segregation and disposal
of biomedical waste as per
guidelines
ICU 1 week • Gain
procien-
cy in ICU
nursing
• Identify
potential
problem and
provide care
accordin-gly
• Record
ndings and
medicati-ons
accurately
• Develop good
IPR with
patient &
family.
- Connect and monitor ECG &
pulse oxymetry
- Assist in endo-tracheal
intubation
- Suctioning -provide care for
a patient on ventilator
- Handling emergency drug
trolly / crash cart.
- Assisting in insertion of
central line and monitoring
Central venous pressure.
- ET suction-ing
- O2 adminis-
tration
Assess skill
with check list
Geriatic
nursing –
medical
/ surgical
/ special
ward
1 week
• Identify
specic
problems
related to the
elderly
• Assist in the
activities of
daily living
• Provide com-
prehensive
nursing care
- Assessment of the geriatric
- Identify the health
problems among the elderly
(psychological, social and
spiritual needs of the elderly)
and provide specic care
- Health promotion of the
elderly
Health teaching
- 1
Assess skill
with check list
Oncolo-gy
Unit
1 week • Provide
carefor
patients with
cancer.
- Screen for common cancers
–Tumor Node Metastasis
(TNM) classication.
- Assist with diagnostic
procedures.
• Biopsies.
• Pap smear
• Provide care
to assigned
patients.
• Assess each
Skill with
checklist.
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale.
94
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
• Counsel and
educate patient
and families.
• Bone-morrow aspiration.
- Assist with therapeutic
procedures.
- Observe various modalities of
treatment.
• Chemotherapy
• Radiotherapy
• Pain management
• Stoma care
• Hormonal therapy
• Immunotherapy
• Gene therapy
• Alternative therapy
- Participate in palliative care.
- Counsel and teach patients
families.
• Observation
report of cancer
unit
• Evaluation of
care plan and
observation
report.
• Completion
of activity
record.
Dermato-
logy and
burns
1 week
• Provide care to
patients with
dermatol-ogy
disorder and
Burn.
• Counsel and
educate patient
and families.
- Assessment of the burn
patient.
• Percentage of burns.
• Degree of burns.
• Dressing
- Fluid & electrolyte
replacement therapy
• Assess
• Calculate
• Replace
• Record
• Intake/output
- Assessment and care of patients
with dermatological disorders.
- Administer topical medications
• Give medicated Baths
- Perform active & passive
exercises.
- Practice medical & surgical
asepsis.
- Counsel & Teach patients and
families
• Provide care
to assigned
patients.
• Health talk - 1
• Assess each
skill with
checklist.
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale.
Ophthalm-
ology
1 week • Provide care to
patients with
Eye disorders.
• Counsel and
educate patient
and families.
- Perform examination of eye.
- Assist with diagnostic
procedures.
- Assist with therapeutic
procedures.
- Perform/assist with irrigations.
- Apply eye bandage.
• Provide care to
2-3 assigned
patients
assessment
using snellen’s
chart
• Assess each
skill with
checklist
Assess
performance
with rating
scale.
95
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
- Apply eye drops/ointments.
- Teach patients and families.
• Observation
reports of
OPD & Eye
bank.
• Assist in
organizing eye
camp
• Evaluation
of
observation
report of
OPD/Eye
bank.
ENT 1 week • Provide care
to patients
with ENT
disorders
• Counsel
and educate
patient and
families
- Perform examination of ear,
nose and throat.
- Assist with therapeutic
procedures.
- Instillation of drops.
- Perform/assist with
irrigations.
- Apply ear bandage.
- Perform tracheostomy care.
- Health education to patients
and families.
• Provide care
to assigned
patients.
• Assess each
Skill with
checklist.
Cardiology
ward /
ICCU /
cardiotho-
racic and
vascular
unit
2 weeks • Provide care
of patients
with cardiac
and vascular
disorders
• Counsel
and educate
patients and
families
- Perform cardio vascular
assessment
- Recording ECG and identify
basic changes in ECG
- Monitoring of patients in on
cardiac monitor
- Preparing and assisting
of frequently performed
diagnostic and therapeutic,
non –invasive and invasive
procedures
- Administer cardiac drugs
- Advanced / Basic Cardiac
Life Support (ACLS/BLS)
- Monitoring and caring for
patients with chest drainage
- Assist in debrillation
- Monitoring of patients in
ICU.
- Maintain ow sheet.
- Perform Endotracheal
suction.
- Demonstrates use of
ventilators, cardiac monitors
etc.
- Physical examination
- Collect specimens and
interprets ABG analysis.
• Plan and
give care to
patients
• Health talk – 1
• Case
presentation –
1
Assessment
of
performance
with rating
scale
96
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
- Assist with arterial puncture.
- Maintain CVP line.
- Pulse oximetry.
- CPR – ALS
- Debrillators.
- Bag- mask ventilation.
- Emergency tray/trolly –
Crash Cart.
- Administration of drugs
• Infusion pump.
• Epidural.
• Intra thecal
• Intracardiac
- Total parenteral therapy
- Chest physiotherapy.
- Perform active & passive
exercises
• Drug
presentation -
1
••
Evaluation
of health
talk, case
presentation
and drug
presentation.
Orthopedic
ward
1 week • Provide
nursing care
to patients
with musculo
skeletal
disorders
• Counsel
and educate
patient and
families
- Assessment of orthopedic
patients
- Assist in the application of
plaster cast and removal of
cast
- Assist in applying skin
traction, bucks extension
traction
- Assist in application and
removal of prosthesis
- Physiotherapy
- Crutch maneuvering
technique
- Ambulation
• Plan and
give care
to assigned
patients
• Nursing care
plan – 1
• Health talk – 1
• Assessment
of
performance
with rating
scale
• Evaluation
of health
talk, case
presentation
and drug
presentation
Communi-
cable
diseases
ward /
isolation
ward
1 week • Provide
nursing
care for
patients with
communi-
cable diseases
- Assessment of patients with
communicable diseases
- Use of personal protective
equipment (PPE)and barrier
nursing
- Health teaching for
prevention of infectious
diseases
- Counseling of HIV/ AIDS
patients
- Counseling of family
members
• Give care
for assigned
patients
• Health talk – 1
• Care plan – 1
• Assessment
of
performance
with rating
scale
• Evaluation
of health
talk, case
presentation
and drug
presentation
97
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
Emergency
ward /
casualty
1 week • Provide care
to patients in
emergency
and disaster
situation.
• Counsel
patient and
relatives for
grief and
bereave-ment
- Practice ‘triage”.
- Assist with assessment,
examination, investigation
& their interpretation, in
emergency and disaster
situations.
- Provide rst aid
- ACLS / BLS
- Assist in legal
documentations and
procedures in emergency
unit.
- Counsel patient and families
grief and bereavement.
• Practice
‘triage”.
• Assess
Performance
with rating
scale.
98
Placement- SECOND YEAR Time- 70 hours
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help students develop the concept of mental health and mental illness, its causes,
symptoms, prevention, treatment modalities and nursing management of mentally ill for individual, family
and community.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the concept of mental health and mental illness and the emerging trends in psychiatric
nursing.
2. Explain the causes and factors of mental illness, its prevention and control.
3. Identify the symptoms and dynamic of abnormal human behavior in comparison with normal human
behavior.
4. Demonstration a desirable attitude and skills in rendering comprehensive nursing care to the mentally
ill.
Total Hours - 70
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
Learning
Activites
Methods of
Assessment
I Describe the
concept of
mental health
and mental
illness in
relation to
providing
comprehensive
care to the
patients.
Introduction
a) Concept of mental health and mental illness
b) Misconceptions related to mental illness
c) Principles of Mental Health nursing
d) Denition of terms used in psychiatry
e) Review of defense mechanisms
f) Mental Health Team
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Structured
discussion
Group
interaction
Short answers
Objective type
II Narrate the
historical
development
of Psychiatry
and psychiatric
nursing.
History of Psychiatry
a) History of Psychiatric Nursing - India and at
international level
b) Trends in Psychiatric Nursing
c) National mental health programme
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Objective type
III Describe
mental health
assessment
Mental Health Assessment
a) Psychiatry history taking
b) Mental status examination
c) Interview technique
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Return
Demonstration
MENTAL HEALTH NURSING
99
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
Learning
Activites
Methods of
Assessment
IV Describe
therapeutic
relationship
Demonstrate
skills in process
recording
Therapeutic nurse-patient relationship:
a) Therapeutic nurse patient relationship:
Denition, components and phases,
Importance
b) Communication skills Denition elements,
types, factors inuencing communication,
barriers (therapeutic impasse)
5 Lecture cum
discussions
Role play
Videos
Demonstration
of process
recording
Short answers
Return
demonstration
V List various
mental disorders
and describe
their mental
and psychiatric
and nursing
management.
Mental Disorders and Nursing Interventions
a) Psycho-Pathophysiology of human behavior
b) Etiological theories (genetics, biochemical,
psychological etc)
c) Classication of mental disorders.
d) Disorders of thought, motor activity,
perception, mood, speech, memory,
concentration, judgment
e) Prevalence, etiology, signs and symptoms,
prognosis, medical and Nursing
management
f) Personality & types of personality related to
psychiatric disorder
g) Organic mental disorders: Delirium,
Dementia
f) Psychotic disorders:
- Schizophrenic disorders
- Mood (affective) disorders: Mania
depression, Bipolar affective
disorders(BPAD)
h) Neurotic disorders: Phobia, anxiety
disorders,obsessive compulsive disorders,
depressive neurosis, conversion disorders,
dissociative reaction, psychosomatic
disorders, post traumatic stress disorder
i) Substance use and de-addiction: alcohol,
tobacco and other psychoactive substance
j) Child and adolescent psychiatric disorder;
- Sleep disorder
- Eating disorders
- Sexual disorders
k) Nursing Management: Nursing process and
process recording in caring for patients with
various psychiatric disorders
25 Lecture cum
discussions
Case study
Case
Presentation
Process
recording
Videos
Role plays
Field visits-
De-addiction
centers, Alcohol
Anonyms group,
Adolescent
clinics, Child
guidance centers
etc
Short answers
Essay types
Case Study
Case
Presentation
100
Unit.
Learning
Objectives
Content Hr.
Teaching
Learning
Activites
Methods of
Assessment
VI Describe the Bio
– psychosocial
therapies and
explain the role
of the nurse
Bio – Psycho & Social Therapies
a) Psychopharmacology – Denition,
classication of drugs antipsychotic,
Antidepressant, antimanic, antian xiety
agents, anti parkinsons
b) Psychosocial therapies – individual
therapies, group therapy, behavior therapy,
occupational therapy, family therapy, melieu
therapy
c) Role of nurse in these therapies.
d) Somatic therapy – Electro Convulsive
Therapy, insulin therapy,
e) Role of nurse in these therapies.
12 Lecture cum
discussions
Seminar
Videos
Demonstration
Field visits-
Rehabilitation
centre, Day care
centres
Role plays
Short Answers
Essay types
Return
demonstration
Quiz
Drug study
VII Describe the
concept of
preventive
community
mental health
services.
Enumerate the
nurse’s role
in National
mental health
programme
Community Mental Health
a) Concept, importance, scope
b) Attitudes , Stigma and discrimination
related to the mentally ill
c) Prevention of mental illness(Preventive
Psychiatry) during childhood, adolescent,
adult hood and old age.
d) Community Mental Health Services.
e) Role of Nurse in national mental health
programme and Psychiatric care in
Community
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Role play
Videos
Short answers
Essay type
Assignment
VIII Explain different
psychiatric
emergencies
and their
management
Demonstrate
skills in crisis
intervention
Psychiatric Emergencies and Crisis
Intervention
a) Types of Psychiatric emergencies: Over
Active, under active patient, Violent
behaviour,
b) Suicide, adverse drug reactions, withdrawal
symptoms, Acute psychosis etc
c) Crisis and its intervention: AIDS,
Adolescent Crisis
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Videos
Role plays
Demonstration
Short answers
Objective Type
Essay type
IX Describe the
legal aspects
to be kept in
mind in the care
of mentally ill
patients.
Forensic Psychiatry / Legal Aspects
a) India Lunatic Act 1912
b) Narcotic Drugs and psychotropic Act 1965,
1985
c) Mental Health Act 1987, 2014
d) Admission and discharge procedures
e) Standards of psychiatric nursing practice.
f) Rights of Mentally ill patients
g) Legal responsibilities in the care of mentally
ill patients.
5 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstration
Short answers
Essay type
Objective Quiz
101
Placement- SECOND YEAR Time – 320 hrs (8 weeks)
Internship 96 hrs (2 weeks)
Areas Duration Objectives Skill Assignments
Assessment
methods
Psychiatric
OPD
3 weeks • Assess patients
with mental health
problems
• Observe and assist
in therapies
• Counsel and educate
patients, and
families
- History taking
- Perform mental status
examination
- Assist in
pyschometric
assessment
- Observe and assist in
therapies
- Teach patients and
family members
• History taking-1
• Mental status
examination-2
• Observation
report of OPD-1
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
checklist
• Assessment
of observation
report
• Completion of
activity record
Child
guidance
clinic
1 week • Assessment of
children with
various mental
health problem’s
• Counsel and provide
health education for
children, families
and signicant
others
- History taking
- Perform mental status
examination
- Observe and assist in
therapies
- Health education of
family members and
signicant others
- Counsel family
members and
signicant others
• Observation
report of child
guidance clinic
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
checklist
• Assessment
of observation
report
Inpatient
ward
6 weeks • Assess patients
with mental health
problems
• Provide nursing
care for patients
with various mental
health problems
- History taking
- Perform mental status
examination
- Observe and assist in
therapies
- Provide nursing care
to the mentally ill
patient
- Health educate
family members and
signicant others
• Assess &
give nursing
care to 2-3
patients with
various mental
disorders
• History taking-1
• Mental status
examination-2
• Case study-1
• Care plan -1
• Case
presentation-1
• Process
recording-2
• Maintain drug
book
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
checklist
• Assessment
of the case
study, case
presentation,
process
recording and
care plan
MENTAL HEALTH NURSING- PRACTICAL
102
Placement- SECOND YEAR Time – 70 hour
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help students develop and understanding of the concept of child health, the trends in
child care and the health problems of children. This shall enable the students to meet the needs of the children,
in health and sickness.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Explain the concept of child health, the principles underlying child care trends in pediatric nursing.
2. Describe normal growth and development of children, so as to recognize deviations for normal health
and care of healthy children
3. Demonstration skill in meeting the needs of the sick infants and children based on the IMNCI guidelines
of GoI
Total Hours: 70
Unit
No.
Learning objective Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Understand the concept
of the child health care,
trends & emerging
challenges for pediatric
nurses
Describe the role of
pediatric nurses in
clinics, hospitals and
community
Introduction
a) Modern concept in child health
care
b) Trends in pediatric nursing
c) Role of pediatric nurses in child
care
d) Emerging challenges, nursing
process related to pediatric
nursing
e) Concept of preventive pediatric
f) Vital statistics related to
pediatrics as per the NRHS and
GoI
5 Lecture cum
discussions
Project on
collection of vital
statistics related
to child health
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
II Describe the normal
growth & development
of children
Growth & Development
a) Denition, principles, factors
affecting growth & development,
techniques of assessment,
plotting of growth chart
15 Lecture cum
discussions
Role play
Videos
Plotting of
growth chart
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
CHILD HEALTH NURSING
103
Unit
No.
Learning objective Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
b) Infant:
Growth & Development, health
promotion, breast feeding
&weaning, immunization, infant
and young child feeding
c) Toddler :
Growth & Development,
nutrition counselling, toilet
training, safety, prevention of
accidents, play.
d) Preschoolers
Growth & development Daycare
centers Role of Parents in sex
education
e) School ager
Growth & development, rest,
sleep, physical exercises &
activity, dental health, sex
education
f) Adolescent
- Growth &development,
adaptation to puberty,
menstrual hygiene, nutritional
guidance, sex education,
- Role of Parents in health
promotion of adolescents
- Control of iron deciency
anemia (WIFS guidelines)
III Describe the role of
nurse in caring for a
sick child
Develop skill in
carrying out nursing
intervention while
caring for pediatric age
group.
The sick child
a) Child’s reaction to hospital
b) Effect of hospitalization on the
family of the child
c) Role of nurse in helping child &
family in coping, with stress of
hospitalization & illness
Pediatric procedures:
a) Preparation of child for
diagnostic tests, collection of
specimens.
b) Calculation & Administration of
oral & parenteral medication
c) Procedures related to feeding
- Katori& Spoon
- Ryle’s tube & gastrostomy
8 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstration
Simulation
Role play
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
104
Unit
No.
Learning objective Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
d) Procedures relating to
elimination
- Enema
- Colostomy irrigation
e) Administration & analysis of
oxygen concentration, steam
inhalation, nebulization,
f) Other procedures:
- Pediatric Resuscitation
- Surgical dressing
IV Describe the
management of
behavioral disorders
and common health
problems of children
Demonstrate skills
in the prevention &
implementation of
medical & nursing
management of
behavioral disorders&
common health
problems.
Disorders and health problems of
a child
a) Infancy :
- Failure to thrive
- Diarrhea & Vomiting
b) Childhood
- Communicable diseases
- Tonsillitis
- Otitis media
- Child abuse
- Breath holding spasms
- Enuresis, nail biting, thumb
sucking, somnambulism
- Protein Energy Malnutrition
- Helminthic infections
- Bites and stings
- Pica
- Tics
c) Adolescent
- Precocious puberty
- Gynecomastia
- Accident, sport injuries
- Obesity & anorexia nervosa
- Juvenile delinquency
6 Lecture cum
discussions
Seminars
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
V Demonstrate
skills in providing
comprehensive nursing
care to the children
having congenital
defects/ malformation
Child with congenital disorders:
Etiology, signs and symptoms,
diagnosis, complications and
medical, surgical & nursing
management of children with:
- Malformations of CNS, cranial
deformities, spina bida,
hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy,
meningocoele.
- Skeletal defects, cleft lip &
cleft palate
15 Lecture cum
discussions
Presentation
of picture of
congenital
anomalies
Supervised
clinical practices
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
105
Unit
No.
Learning objective Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
- Gastro intestinal tract
defects, stula, anorectal
malformations, hernia
- Congenital hypertrophied
pyloric stenosis
- Defects of Genito-urinary Tract
–hypospadiasis & epispadiasis,
extrophy of bladder,
phimosis & paraphimosis,
cryptorchidism, polycystic
kidney
- Sexual abnormalities,
ambiguous genitalia
- Defects of cardio vascular
system, cyanotic and
acyanotic- TOF (Tetralogy of
Fallouts), TGV (Transposition
of Great Vessels), TAPVC,
ASD, VSD, Coactation of
aorta, PDA
- Orthopedic abnormalities -
congenital talipusequinovarus,
congenital dislocation of hips
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Down’s syndrome, Turner’s
syndrome.
VI Demonstrate
skills in providing
comprehensive nursing
care to children with
various disorders &
diseases
Children with various disorders
and diseases
Etiology, signs and symptoms,
complications, prevention, medical,
surgical &nursing management of :
a) Renal System
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Acute Glomerulonephritis
- ARF & CRF
b) Resp. System
- URI and LRI
- Asthma, Pneumonia
c) GI System
- Intestinal obstruction
(Mechanical)
- Hirschsprung’s disease
- Malabsorption Syndrome
- Inammatory conditions
– appendicitis, Meckel’s
divertculum, ulcerative colitis
- Worm infestation
15 Lecture cum
discussions
Presentation
Clinical teaching,
Simulation,
Videos,
Visit to Blind,
Deat & dumb
school &
rehabilitation
centre
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
106
Unit
No.
Learning objective Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
d) CVS System
- Rheumatic fever
- CCF
- Infective endocarditis
e) Hematological System
- Anemia
- Leukemia,
- Thalassemia
- Hemophilia
- Sickle cell anemia
- Thrombocytopenic purpura
f) Neurological System
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Convulsive disorders
- Cranio-cerebral trauma
g) Endocrine
- Pituitary disorders
- Hypo & Hyperthyroidism
- Juvenile Diabetes
- Adrenal disorders
h) Developmental problem
- Handicapped children
- Mental Retardation
- Dyslexia
- Hearing & Vision impairment
i) Others:
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalance
- Burns
j) Problems with locomotion:
- Poliomyelitis
- Osteomyelitis
- Kyphosis, lordosis, scoliosis
- Fractures
k) Pre and post operative care of
children undergoing surgery.
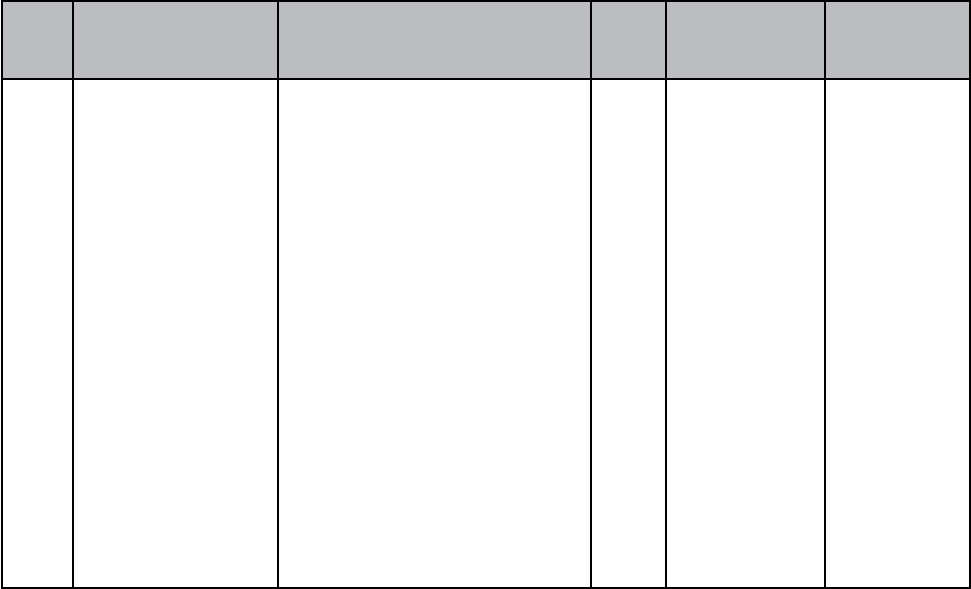
107
Unit
No.
Learning objective Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
VII Describe the various
child welfare
services provided by
Governmental &non
Governmental agencies
Explain the ethical &
legal implication in
pediatric nursing
Child welfare services
a) Child welfare services and
agencies:
- ICDS
- Mid-day meal program
- Balwadi, anganwadi
- Day care centers
- NPSP
b) Law pertaining to Pediatrics:
- National child labour policy
- Child act.
- Juvenile justice act
- Internationally accepted rights
of the child
- Rehabilitation of delinquent &
destitute children
- Adoption laws and services
- Adolescent health programs
– menstrual hygiene, WIFS
program, adolescent safety
program
6 Lecture cum
discussions
Visit to
anganwadi
schools, remand
homes &
adoption centers
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
108
Placement- THIRD YEAR Time – 320 hrs (8 weeks)
Internship 96 hrs (2 weeks)
Areas Duration Objectives Skill *Assignments
Assessment
methods
Paediatric
medicine
ward
3 weeks • Perform physical
assessment
• Assist in diagnostic
procedure and
provide pre and
post care related
to diagnostic
procedure
• Administer the
drugs • Provide
health education
• Perform basic
resuscitation
- Taking pediatric
History
- Perform physical
examination and
assessment of
children
- Administration of
oral, I/M, & I/V,
medicine/ uid
- Calculation of uid
requirements
- Prepare different
strengths of I.V.
uids
- Apply restraints
- Administer O2
inhalation by
different methods
- Feed children by
katori (bowl) and
spoon,pallada etc.
- Collect specimens
for common
investigations
- Assist with common
diagnostic procedure
- Teach mothers/
parents on balance
diet for child of
different age group
- Oral rehydration
therapy
- Feeding & weaning
- Play therapy
- Check vital signs
- Give enema
- Insert suppositories
Give care
to assigned
paediatric
patients Nursing
care plan-1
Case study or
Presentation-1
Health talk-1
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
checklist
• Evaluation of
Nursing care
plan, Case
study, Health
talk, Case
presentation
• Completion of
activity record
CHILD HEALTH NURSING- PRACTICAL
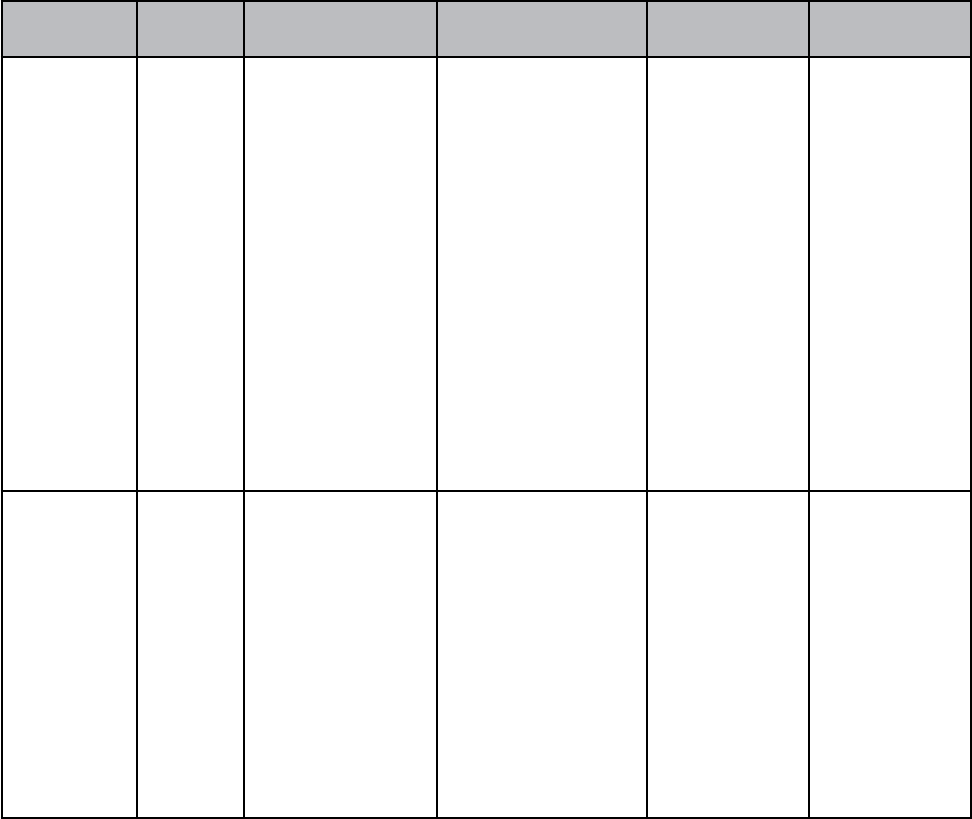
109
Areas Duration Objectives Skill *Assignments
Assessment
methods
Paediatric
surgery ward
3 weeks • Recognize
different pediatric
surgical condition
• Provide pre and
post operative
care to children
with common
paediatric surgical
conditions/
malformation
• Counsel and
educate parents
- Do bowel wash
- Care for ostomies:
• Colostomy
irrigation
• Ureterostomy
• Gastrostomy
• Enterostomy
- Urinary
catheterization and
drainage
- Feeding
• Nasogastric
• Gastrostomy
• Jejunostomy
- Care of surgical
wound dressing
- Suture removal
• Give care to
three assigned
paediatric
surgical
patients
• Nursing care
plan-1
• Case study or
presentation-1
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Assess each
skill with
checklist
• Evaluation of
Nursing care
plan, Case
study, Case
presentation
• Completion of
activity record
Paediatric
OPD/
Immuniza-
tion room/
well baby
clinic /
adolescent
clinic
4 weeks • Perform
assessment of
children, health
development and
anthropometric
• Perform
immunization
• Give health
education/
nutritional
education
- Assessment of
children
- Health assessment
- Developmental
assessment
- Anthropometric
assessment
- Immunization
- Health/ nutritional
education
• Health
assessment of
the child
• Health talk - 1
• IMNCI Module
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale
• Completion of
activity record
• Assessment of
the health talk.
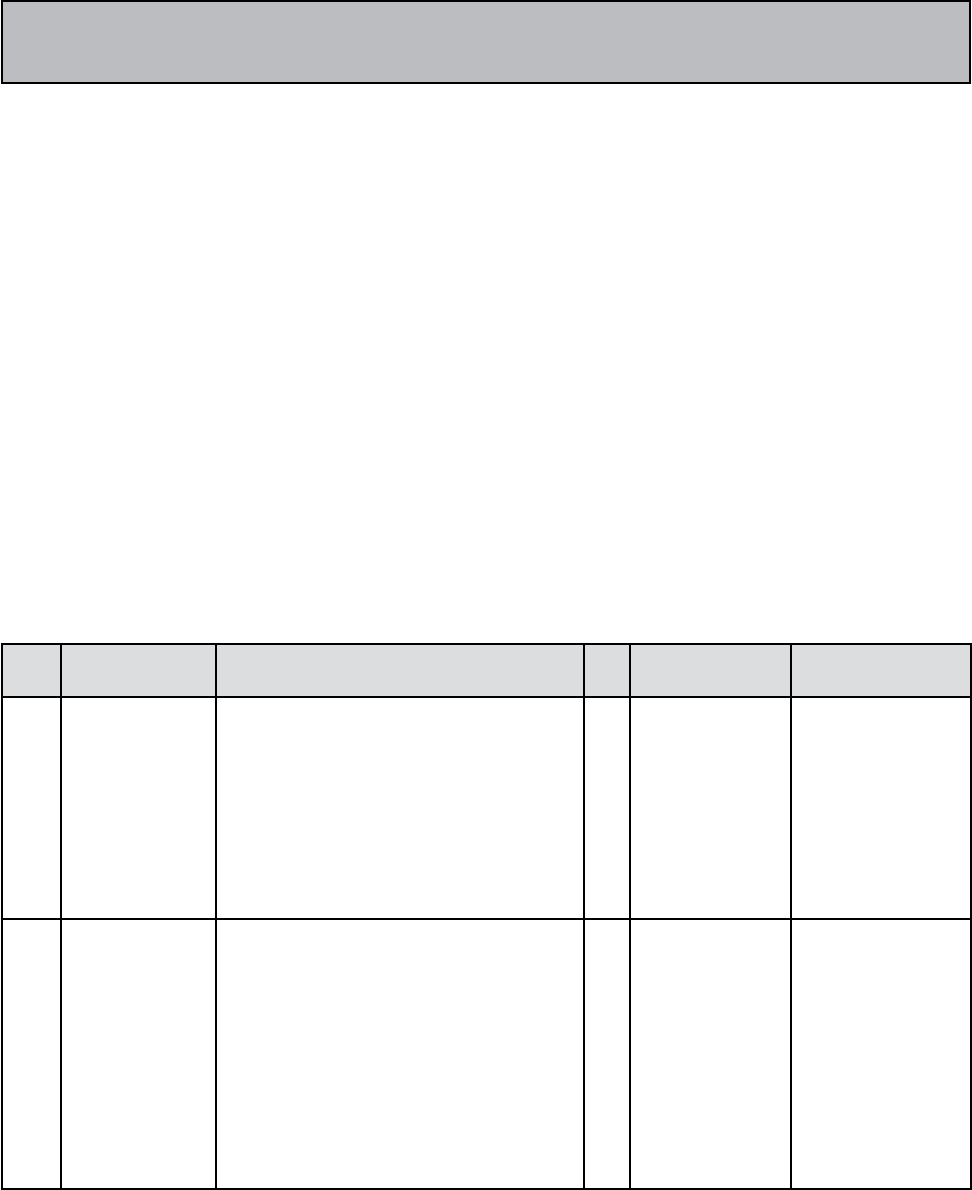
110
Placement- THIRD YEAR Time- 140 hours
Midwifery- 120 hours
Gynecological Nursing- 20 hours
MIDwIFERY
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help students acquire knowledge and gain skills to meet the needs of women during
pregnancy, labor and puerperium and care for the newborn.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the health needs of women in pregnancy, labour and puerperium.
2. Identify deviation(s) from normal pregnancy, labour and puerperium and take appropriate action.
3. Demonstrate skills in providing antepartum, intrapartum and postpartum care to the mother as well as
care to the new born as per the SBA guidelines of Government of India.
Total Hours:120
Unit
No.
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teching learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
I Describe the
scope and trends
in midwifery
Introduction:
a) Denition of midwifery and obstetrical
nursing
b) Scope of midwifery
c) Basic competencies of a midwife
d) History of midwifery
e) Trends of maternity services in India
f) Vital statistics related to maternal health
in India.
4 Lecture cum
discussions
Videos
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
II Describe the
anatomy and
physiology
of female
reproductive
system
Reproductive system
a) Review of structure and function of
female reproductive system
b) Female pelvis –structure, types and
diameters
5 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstrations
Charts,
Specimen
Models &
Objects
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Viva
MIDwIFERY AND GYNECOLOGICAL NURSING
111
Unit
No.
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teching learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
III Describe
the stages of
Embryological
and fetal
development
Embryology and foetal development
a) Oogenesis, spermatogenesis,
fertilization and implantation.
b) Embryology and Fetal development
c) Placenta and membranes:
- Structure
- Functions
- Abnormalities
- Liquor amni
- Umbilical cord
d) Fetal skull:
- Structure
- Diameters
- Fontanels and sutures
e) Fetal circulation
8 Lecture cum
discussions
Charts
Models &
Objects
Specimens
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Oral presentation
IV Describe the
physiological
changes in
pregnancy and
the management
of normal
pregnancy
Demonstrate
skill is caring for
pregnant women
Normal pregnancy and its management
a) Pre-conception care
b) Genetic counseling
c) Physiological changes in pregnancy
d) Diagnosis of pregnancy
- History
- Signs & symptoms
e) Antenatal care:
- History taking
- Calculation of expected date of
delivery,
- Examination and investigations
- Health Education and counselling
- Drugs and immunizations
f) Minor disorders and their management
12 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstration
Clinical teaching
Simulation
Charts & Videos
SBA module of
government of
India, handbook
for staff nurses
(Government of
India)
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
V Describe the
various stages
of labour and
the role of the
midwife in
caring for a
woman in labour
Demonstrate
skill in
conducting the
normal delivery
Normal labour and its management
a) Denition and stages
b) Causes and signs of onset of labour
c) True and false labour
d) First stage of labour:
- Physiology
- Monitoring using partograph and its
interpretation
- Care of mother : physical and
psychological
- Pain management
- Setting up of the labour room
including newborn corner
18 Lecture cum
discussions
Demonstrations
Case studies
Simulation
Videos
Exercises SBA
module of
government of
India, handbook
for staff nurses
(Government of
India)
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
112
Unit
No.
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teching learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
e) Second stage:
- Physiology and mechanism
- Monitoring
- Conduction of normal delivery
- Episiotomy
- Essential newborn care
f) Third stage:
- Physiology and signs
- Active management of third stage
- Examination of the placenta
- Episiotomy suturing
g) Fourth stage:
- Physiology
- Care of the mother and baby
- Postpartum family planing
VI Describe the
management of
normal newborn
Development of
skill in caring
for the normal
newborn
Management of newborn
a) Assessment
b) Physiological adaptation
c) Apgar scoring
d) Examination for defects
e) Breast feeding- BFHI
f) Care of newborn -Skin, eyes,
buttocksetc
g) Bonding and rooming in
h) Minor disorders of new born:
- Birth marks, rashes, skin
- Infections, sore buttocks,
- Infection of eyes.
14 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstrations,
Clinical teaching
Chart
Videos
SBA module,
ENBC, NSSK,
PPIUCD module,
handbook for
staff nurses of
government of
India
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
VII Describe normal
pureperium
and the role
of midwife
in the caring
for woman in
puerperium
Management of normal puerperium
a) Denition and objectives of care
b) Physiological changes
c) Postnatal counselling
d) Lactation and feeding
e) Care during puerperium – breast and
perineal care, postnatal exercise,
postnatal examination, follow up,
family welfare
f) Minor ailments and management.
g) Family planning
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Simulation
Role play
SBA module,
PPIUCD module,
handbook for
staff nurses of
government of
India
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
113
Unit
No.
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teching learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
VIII Describe the
complications
of pregnancy
Demonstrate
skills in
providing care
for women with
complicated
pregnancy
Management of complications during
pregnancy
a) Bleeding in pregnancy
- Early and late
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Abortion
- Antepartum hemorrhage
- Vesicular mole
b) Hyperemesis gravidarum
c) Gestational diabetes mellitus
d) Pregnancy inducedhypertension
- Pre eclampsia
- Eclampsia
e) Hydromnios – poly and oligo
f) Pelvic inammatory diseases
g) Intra uterine growth retardation
h) Post maturity
i) Intra uterine death
High risk pregnancy:
- Monitoring- NST, USG
- Anemia
- Jaundice
- Viral
- Urinary tract infections
- Hearts diseases
- Diabetes
- AIDS and STD’s
- Osteomalacia,
- Teenage pregnancy
- Elderly Primigravida
- Multipara
- Multiple pregnancy
12 Lecture cum
discussions
Case presentation
Clinical teaching
Videos
Simulation
Case studies and
exercises SBA
module
Short answers
Essay type
Objective type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
IX Describe the
management
high risk labour
Demonstrate
skills in early
detection
and prompt
management of
high risk labour
Management of high risk labour
a) Malposition, malpresentations
b) Contracted pelvis
c) Abnormal uterine actions
d) Cervical Dystocia
e) Premature rupture of membranes,
precipitate and prolonged labour,
induction of labour obstructed labour,
f) Obstetrics Emergencies-Cord prolapse,
cord presentation, amniotic uid
embolism, obstetric shock,rupture of
uterus, shoulder dystocia, vasa previa.
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Bed-side clinic
Videos & Charts
Clinical teaching
IMPAC module
of WHO
MCPC module of
Government of
India
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
114
Unit
No.
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teching learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
g) Complications of third stage
- PostpartumHemorrhage
- Atonic uterus
- Injuries to the birth canal
- Retained placenta and membranes
- Inversion of uterus
X Describe the
puerperal
complications
Demonstrate
skill in the
management of
complications of
puerperium
Management of complications of
puerperium
- Puerperal pyrexia
- Puerperal Sepsis
- Thrombophlebitis and Embolism
- Breast engorgement, Mastitis, Breast
abscess
- Puerperal psychosis
4 Lecturer cum
discussion
Demonstration
Clinical teaching
MCPC module of
Government of
India
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
XI Describe the
management of
high risk and
sick newborn
Demonstrate
skills in caring
for high risk and
sick newborns
High risk and sick newborn
a) Assessment
b) Nursing care
c) Management of newborn with:
- Hyperbilirubinaemia
- Neonatal hypoglycemia
- Hypothermia
- Neonatal Convulsions
- Rh incompatability
- Small for dates
- Low birth weight
- Preterm
- Asphyxia,RDS
- Sepsis
- Birth injuries Cephal hematoma Caput
succedaneum Facial &Erb’s palsy
Torticollis Hemorrhage
- Congenital anomalies
d) Newborn of HIV positive mother,
diabetic mother
e) Levels of care in NICU
10 Lecturer cum
discussion
Demonstration
Clinical teaching
IMNCI module
SBA module
NSSK module
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
115
Unit
No.
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teching learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
XII Describe
the obstetric
operations and
midwife role in
assisting with
each one
Obstetric operations
a) Denition, indication and care of
women undergoing
- Induction of labour
- Manual removal of placenta
- Version
- Forceps delivery
- Vacuum extraction
- Caesarean Section
- Sterilization
- Destructive surgeries
- Amnio infusion
- Manual Vaccum Aspiration, Dilatation
and Evacuation, Dilatation and
Curettage
b) Post abortion care.
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Videos
Post abortion care
module of GoI
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Assessment of skill
using checklist
XIII Describe the
midwife’s
role in the
administration
of drugs for
women during
pregnancy.
labour and post
parturn period
Drugs used in obstetrics
a) Indication, dose, action,
contraindication, side effects and
responsibilities in the administration of :
- Oxytocin
- Uterotonics
- Tocolytics
- Antihypertensives
- Anticonvulsants
- Anesthesia and analgesia
b) Drugs used for newborn
c) Teratogens – effects of drugs on mother
and baby.
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Drug presentation
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
XIV Describe the
ethical & legal
issues related to
midwifery
Ethical and legal aspects related to
midwifery
a) Maternal and newborn death review
b) Mother and child tracking system
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Presentation
Short answers
Objective type
116
GYNECOLOGIAL NURSING
Course objective
The students shall be able to identify different gynecological disorders and diseases and gain skills in
providing nursing care to women suffering from them.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. List different gynecological problems and demonstrate skills in providing nursing care to women
suffering from these disorders and diseases.
Total Hours:20
Unit
No
Learning
objectives
Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
assessment
I Dene the
terms used in
gynecology
Demonstrate
the skills of
gynecology
history taking,
conducting
examination &
investigation
Introduction
a) Denition of terms
b) History
c) Examination
d) Investigation
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Demonstration
Videos
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Return
demonstration
II Describe the
physiology,
psychology and
pathology of
puberty
Puberty
a) Denition
b) Development of sex organs in
females and sexuality
c) Review of menstrual cycle
d) Premenstrual syndrome
e) Disorders of menstruation,
dysmenorrhoea, cryptomenorrhoea,
dysfunctional uterine bleeding
3 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Videos
Charts
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
III Describe the
management
of couples with
fertility related
problems.
Fertility and infertility
a) Denition
b) Causes-both in male and female
c) Investigation
d) Management
e) Articial reproductive techniques
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching,
Videos
Role play
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
117
Unit
No
Learning
objectives
Content Hours
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
assessment
IV Demonstrate
skills in the
management
of clients with
various pelvic
infections.
Pelvic infections
a) Vulva – vulvitis, bartholinitis
b) Vagina - Vaginitis, Trichomonas
vaginitis, Moniliasis,
c) Metritis,Salpingitis, Oophritis
d) Cervical erosions
e) Pelvic Abscess
f) Chronic infection
g) Pelvic inammatory disease
h) Pelvic tuberculosis
i) Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- Warts
- HIV
j) Syndromic case management
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching
Videos
Prevention of STI
module of NACO
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
V Describe the care
of women with
gynaecological
disorders
Gynaecological disorders
a) Retroversion, retro exion
b) Fistulas
c) Uterine displacement & prolapse
(Procidentia)
d) Uterine malformations
e) Cysts and broids
f) Uterine polyps
g) Tumors of the reproductive tract –
benign and malignant
h) Palliative care and rehabilitation
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Case
Presentation
Demonstration
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
VI Describe the care
of the woman
with breast
disorders
Breast disorders
a) Review mastitis, breast engorgement,
breast abscess
b) Tumors of the breast benign and
malignant
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Clinical teaching,
Videos
Role play
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
VII Describe the care
of women with
menopause
Menopause
a) Denition and physiological changes
b) Signs and symptoms
c) Health education and counselling
d) Hormone replacement therapy
e) Surgical menopause
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Case histories.
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
118
Placement: THIRD YEAR (PART – I) Time: 560 hours
Internship: 384 hours
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
Antenatal
clinic / ward
3 weeks • Assessment of
pregnant women
• Counselling of
AAntenatalmo-
thers
- Diagnose pregnancy using
pregnancy detection kit
(preg-card)
- Antenatal history taking
- Physical examination
- Antenatal examination –
abdomen and breast
- Recording weight and BP
- Hemoglobin estimation
- Urine testing for sugar and
albumin
- Immunization
- Assessment of risk status
- Antenatal counselling
- Maintenance of antenatal
records
- SBA module
• Conduct
antenatal
examinations
– 20
• Health talk – 1
• Case study – 1
Verication of
the ndings
of antenatal
examinations
Assessment
of skills using
checklist
Labour room 6 weeks •Assess the woman
in labour
• Carry out
pervaginal (PV)
examinations
• Monitor women
in labour
• Conduct normal
deliveries
• Perform
episiotomy and
suture it
• Resuscitate
newborns
- Assessment of woman in
labour
- Vaginal examinations (PV)
and their interpretation
- Monitoring women in
labour using the partograph
- Caring for women in labour
- Setting up of the labour
unit including the newborn
corner
- Conduct normal delivery
including active
management of third stage
of labour (AMTSL)
- Provide essential newborn
care
- Immediate newborn
assessment
- Resuscitation of the
newborn.
- Assessment of the risk
status of the newborn
- Episiotomy and suturing
• Perform
pervaginal
examinations
– 5
• Conduct normal
deliveries – 20
• Perform
and suture
episiotomies – 5
• Resuscitate
newborns – 5
• Witnessing
abnormal
deliveries - 5
• Case book
recording
Assessment
of clinical
performance
with rating scale
Assessment of
each skill with
checklist.
Practical
examination
MIDwIFERY & GYNAECOLOGICAL NURSING- PRACTICAL
119
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
- Administration of
uterotonic drugs – oxytocin
, misoprostol
- Administration of
magnesium sulphate.
- Maintenance of labour and
birth records
- SBA module
Operation
theatre
2 week • Prepare and assist
with caesarean
section, MTP,
tubectomy and
other surgical
procedures
- Preparation for caesarean
section and other surgical
procedures
- Assist in caesarean section
- Prepare and assist in MTP
procedures
- Prepare and assist for
tubectomy
• Assist with
caesarean
section – 2
• Case book
recording
Assessment
of skill with
checklist.
Postnatal
ward
5 weeks • Provide nursing
care to postnatal
mother and the
baby
• Counsel and
teach mother
and family for
parenthood
- Examination and
assessment of mother and
the baby
- Identication of deviations
- Care of postnatal mothers
and baby
- Perineal care
- Breast care
- Lactation management
- Breast feeding
- Kangaroo mother care
(KMC)
- Immunization
- Teaching postnatal
mother on mother craft,
post natal care, exercise,
immunization
• Provide
postnatal care
to mothers and
babies – 20
• Health talks – 1
• Case study – 1
• Case
presentation - 1
Assessment
of clinical
performance
with rating scale
Assessment of
each skill with
checklist.
Practical
examination
NICU 4 weeks • Provide nursing
care to newborns
at risk
- Newborn assessment
- Admission of neonates
- Feeding of high-risk
newborn :- katori spoon,
paladai, tube feeding, total
parentral nutrition
- Thermal management of
newborns – kangaroo
mother care, care of baby
in radiant warmer and
incubator.
- Monitoring and care of
neonates
• Case study - 1
• NSSK Module
Assessment
of clinical
performance
with rating scale
Assessment of
each skill with
checklist.
Practical
examination
120
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignment
Assessment
methods
- Administration of
medications
- Intravenous therapy
- Assisting in diagnostic
procedures
- Assist in exchange
transfusion
- Care of baby in ventilator,
phototherapy,
- Practice infection control
protocols
- Health education and
counselling of parents
- Maintenance of records and
reports
Family
welfare clinic
2 week • Counsel for and
provide family
welfare services.
- Family planning
counselling techniques
- Insertion of IUCD
- Teaching by demonstration
on the use of different
family planning methods
- Arrange for and assist with
family planning operations
- Maintenance of records and
reports
• IUCD insertion
– 5
• Family planning
counselling – 2
Assessment
of clinical
performance
with rating scale
Assessment
of each skill
with checklist.
Practical
examination
Gynaeco-
logy ward
2 weeks • Provide care for
patients with
gynecological
disorders.
• Counsel and
educate patient
and families.
- Assist with gynecological
examination.
- Assist and perform
diagnostic and therapeutic
procedures.
- Teach women on breast self
examination (BSE)
- Health education on
perineal hygiene and
prevention of sexually
transmitted infections
- Pre and post operative care
of women undergoing
gynecological surgeries
- Menopause counseling
• Provide care
to assigned
patients.
• Nursing care
plan- 1.
• Menopause
counseling – 1
• Assess each
skill with
checklist.
• Assess
performance
with rating
scale.
• Evaluation of
care plan.
121
Placement: THIRD YEAR (PART – I ) Total Hours: 90
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help students to practice community health nursing for the individual, family and groups
at both the urban and rural settings by using concepts and principles of health and community health nursing.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the studentsshallbeable to:
1. Describe the health system and health care services in India.
2. Identify major health problems, national health programmes and specialized community health
services.
3. Explain the concept of health team and describe the nurses’ role at various levels of health care
setting.
4. Demonstrate skills in rendering effective nursing care to the individual, family and groups in all
community health settings.
Total Hours: 90
Unit
Learning
objective
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
I Explain the
health system in
India
Heath system in India
Organization and administration of health
system in India at
a) Central level
- Union Ministry
- Directorate General of Health Services
- Central Council of Health
b) State level
- State Health Administration
- State Ministry of Health
- State Health Directorate
c) District level
- Sub Divisions
- Tehsils/ Talukas
- Villages
- Municipalities & Corporation
- Panchayats
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Organizational
chart of various
levels
Visit to
Municipality
Ofce, Panchayat
ofce, Health
block ofce,
CHC
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING-II
122
Unit
Learning
objective
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
II Describe the
health care
services in India
and discuss the
role of the nurse
in these services
Health care delivery system
a) Heath care concept and trends
b) Health care services - Public sector, Rural,
Urban
c) Private sector
d) Public Private Partnership (PPP)
e) Other agencies
f) Indigenous systems of medicine Ayurvedha,
yoga, unani, siddha and homeopathy
(AYUSH)
g) Voluntary health services
h) National Health Programmes
i) Nurse role in health care services
8 Lecture cum
discussion
Visit to different
health care
agencies
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
III Describe health
planning in India
Health planning in India
a) National health planning
b) Five year plans
c) Health Committees and reports
d) National health policy
10 Lecture cum
discussion and
reports
Short answer
Essay type
IV Describe
the different
specialized
community
health services
and the nurse’s
role in these
services
Specialized community health services and
nurse’s role
a) RCH (reproductive health and child care)
b) National Health Mission (rural/ urban)
c) Janani Sishu Suraksha Karaykaram (JSSK)
d) Emergency ambulance services.
e) Government health insurance schemes
f) School health Services
g) Occupational health nursing (including
health care providers)
h) Geriatric nursing
i) Care of differently abled- Physical and
mental
j) Rehabilitation nursing
18 Lecture cum
discussion
Visit to different
agencies of
specialized
services, factory,
Old age home,
Homes for the
differently abled
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
V Describe the
major health
problems in India
National health problems
Health Problems in India
a) Communicable diseases
b) Non communicable diseases
c) Nutritional problems
d) Environmental sanitation
e) Population
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Quiz
Short answer
Objective type
VI Describe the
national health
and family
welfare programs
in India and the
role of the nurse
National Health programme:
- National ARI program
- Revised national tuberculosis control
program (RNTCP)
- National anti-malaria program
- National larial control program
15 Lecture cum
discussion
Government of
India program
yers.
Short answer
Objective type
123
Unit
Learning
objective
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
- National guinea worm eradication
program
- National leprosy eradication program
- National AIDS control program
- STD control program
- National program for control of blindness
- Iodine deciency control program
- Expanded program of immunization
- National family welfare program
- National water supply and sanitation
program
- Minimum needs program
- National diabetes control program
- Polio eradication : pulse program
program, NPSP
- National cancer control program
- Yaws eradication program
- National nutritional anemia prophylaxis
program
- 20 point program
- ICDS program
- Mid –day meal program
- National mental health program
- Adolescent health program
- Role of nurse in the national health
programme.
VII Explain the
meaning of
demography
and describe
the national
family welfare
programmes
.
Demography and family welfare
a) Demography
- Concept
- Trends in the world and in India
- Concept of fertility and infertility
- Small family norm
b) Family Welfare
- Concept, importance, aims & objectives
- Family planning methods
- Family planning counseling
- National family Welfare Policy
- National family Welfare Programme
- Role of a nurse in the family planning
programme
18 Lecture cum
discussion
Show and
explain family
planning devices
Role play
Demonstration
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
124
Unit
Learning
objective
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
Activities
Assessment
methods
VIII Describe the
concept and
functions of
health team
and the role
of nursing
personnel at
various levels.
Health Team:
a) Concept
- Composition
- Functions
b) Role of Nursing personnel at various levels:
- District Public Health Nursing Ofcer
- Block health Nurse
- Public Health Nurse
- Lady Health Visitor/ health supervisor
- Health worker female/ ANM
7 Lecture cum
discussion
Interaction with
health team
members: Job
description as per
the Indian Public
Health Standards
(IPHS)
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
IX Explain the
concept and
uses of health
information
system
Health Information System
a) Concepts, components, uses , sources.
b) Vital Statistics:
- Important rates and indicators
c) Vital health records and their uses.
d) Basic statistical methods
e) Descriptive statistics
6 Lecturer cum
discussion
Exercises
Short answer
Objective type
Exercises
X Describe the
national and
international
health agencies
Health Agencies
a) International:
- WHO
- UNFPA
- UNDP
- World bank
- FAO
- UNICEF
- DANIDA
- European commission (EU)
- Red cross
- USAID
- UNESCO
- ILO
- CARE
b) National:
- Indian Red Cross
- Indian Council for child welfare
- Family Planning association of India
- Other NGOs
3 Lecture cum
discussion
Seminar
Short answer
Objective type
125
Placement: THIRD YEAR- PART I Time: Practical – 160 hours
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignments
Assessment
Methods
Community
Health
Nursing II-
4 wks
urban /
rural
• Organize and conduct
clinics
- Antenatal
- Postnatal
- Family welfare.
- Under ve.
• Diagnose health
needs and provide
domiciliary care for
antenatal and postnatal
mothers.
• Assess health needs
of family; plan and
carry out treatment
for minor ailments;
identify need for
referral and refer.
• Plan, conduct and
follow up health
education.
• Assist in conducting
camps and participate.
• Maintain records and
reports in PHC.
• Assist in family
welfare services and
conduct need based
health education.
• Participate in school
health programme.
• Counsel and educate
eligible couple, family
and community.
- Assisting in set-up and
conduct of the clinics:
- Providing domiciliary
care to the antenatal and
postnatal cases using
bag and / or Domiciliary
Obstetric Kit.
- Performing nursing care
at home.
- Preparing and conducting
Health Teachings on
Reproductive and Child
Health ( RCH) Care
Issues.
- Assisting in organizing
Camps.
- Maintaining records and
reports at Primary Health
Centre.
- Assisting in activities of
Family Welfare.
- Participating in School
Health Services.
• Health talk- 2
• Family
Health
Nursing care
plan-2
• Group
project-1
• Daily
Dairy-1
• Report on
school health
program
- Internal
examina-tion
(1st& 2nd
term)
- Pre Council
examina-tion
- Assessment
of performa-
nce with
rating scale
- Evaluation of
- Assignme-nts
- Field visit
reports
- Daily diary
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING II- PRACTICAL
Area Duration Objectives Skills Assignments Assessment Methods
Urban /
rural
6 weeks Provide
comprehensive care to
individual family and
community
Comprehensive nursing
care to the individual ,
family and community
Integrated
practice and
group project
Health talk – 2
Nursing care plan
– 2
Assessment of
clinical performance
with rating scale
Evaluation of group
project.
Placement- INTERNSHIP (THIRD YEAR PART-II) Time- 288 Hours
126
Placement: Internship (3rd years Part II) Time: 120 Hours
Nursing Education- 20 hours
Introduction to Research- 30 hours
Professional Trends and Adjustment- 30 hours
Nursing Administration and Ward Management- 40 hours
NURSING EDUCATION
Course Description:-
This course is designed to introduce the students to the concept of teaching as an integral part of nursing
practice.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Explain the concept of teaching
2. Describe techniques used for teaching.
Total Hours: 20
Unit
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
activities
Method of
Assessment
I Describe the
concept of
education
Introduction
a) Education
- Meaning, aims, scopeand purposes,
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answers
Objective type
II Explain the
process of
teaching and
learning
Teaching learning process
a) Basic principles
b) Characteristics of teaching and learning
c) Teaching responsibility of a nurse
d) Preparation of teaching plan
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answers
Objective type
Evaluation of
teaching plan
III Narrate the
methods of
teaching Describe
the clinical
teaching methods
Methods of teaching
a) Methods of teaching
b) Clinical teaching methods
- Case method
- Bed side clinic
- Nursing rounds
- Nursing conference ( individual and
group)
- Process recording.
14 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Objective type
Evaluation of
planned as well as
incidental health
teaching
NURSING EDUCATION, INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH,
PROFESSIONAL TRENDS & ADJUSTMENT & NURSING
ADMINISTRATION & wARD MANAGEMENT
127
INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH
Course Description:-
This course is designed to develop fundamental abilities and attitude in the students towards scientic
methods of investigation and utilization of research nding so as to improve practice of nursing.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the use of research in the practice of nursing
2. Describe the scientic methods of investigation used in nursing.
3. Participate in research activities in the health care settings.
Total Hours: 30
Unit
Learning
Objectives
Contents Hr.
Teaching learning
activities
Assessment
Method
I Discuss the
importance
of research in
Nursing
Introduction
a) Denition
b) Terminology related to research
c) Need and importance of nursing
research
d) Characteristics of good research
3 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answers
Objective type
II Describe the
research process
Research process
a) Purposes and objectives
b) Steps in research process
3 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Essay type
III Describe the
various research
approaches
Research approaches and designs
a) Types
b) Methods
c) Advantages and disadvantages
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Essay type
IV Describe the
various data
collection methods
Data collection process
a) Meaning
b) Methods and instruments of data
collection
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Essay type
V List the steps
involved in data
analysis
Analysis of data
a) Compilation
b) Tabulation
c) Classication
d) Summarization
e) Presentation and interpretation of data
using descriptive statistic
6 Lecture cum
discussion
Reading the
research articles
Short answer
Essay type
VI Describe the
importance
of statistics in
research
Introduction to statistics
a) Denition
b) Use of statistics
c) Scales of measurement
d) Frequency distribution
e) Mean, median, mode and standard
deviation.
6 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Essay type
VII Describe the
utilization of
research in nursing
practice
Utilization of research in nursing practice
- Evidence based practice
2 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Essay type
128
PROFESSIONAL TRENDS AND ADJUSTMENT
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help students develop an understanding of the career opportunities available for
professional development.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe nursing as a profession.
2. Identify various professional responsibilities of a nurse.
3. Describe various professional organizations related to nursing.
4. Identify the need for in-service and continuing education in nursing
5. Demonstration skills in application of knowledge of professional etiquettes in the practice of nursing
in any health care setting.
Total Hours: 30 hours
S. No
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Describe nursing
as a profession
Nursing as a profession
a)
Denition of profession
b) Criteria of a profession and nursing
profession
c) Evolution of Nursing Profession in India
d) Educational preparation of a professional
nurse
e) Qualities/ Characteristics and role of a
professional nurse
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Objective type
Essay type
II Explain various
aspects of
Professional
ethics
Professional ethics
a)
Meaning and relationship of professional
ethics and etiquettes
b) Code of ethics for nurse by ICN
c) Standards for nursing practice (INC)
d) Etiquettes for employment: locating
posting, applying and accepting a
position, resignation from a position.
6 Lecture cum
discussion
Assignment:
Application for
job acceptance &
job resignation
Short answer
Essay type
III Discuss the
importance
of continuing
education in
personal and
professional
development
Personal and professional development
a)
Continuing education
- Meaning and importance
- Scope
- Identifying opportunities
10 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Essay type
129
S. No
Learning
objectives
Contents Hr.
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
b)
Career in Nursing
- Opportunities available in Nursing in
Hospital, Community teaching and
other related special organization.
c)
In-service education
-
Denition
-
Value
-
Need participation in committee
procedures
- Nursing in the future
Draw a career
ladder in nursing
in reference to
international
inuence and
nancial aid.
IV Discuss the
signicance of
legislation in
Nursing
Legislation in nursing
a)
Purpose and importance of laws in
Nursing
b) Legal Terms
c) Common legal hazards in Nursing
d) Laws and regulations related to health
care providers in India at different levels
e) Service and institutional rules
f) Regulation of nursing education
g) Registration and reciprocities
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Assignment
V List the various
organizations
related to health
and nursing
profession and
briey describe
their function
Profession and related organizations
a)
Regulatory bodies: Indian Nursing
Council, State Nursing Council
b) Professional organizations:
- Trained Nurses Association of India,
- Students Nurses Association,
- Nurses League of the Christian
Medical Association of India,
- International Council of Nurses (ICN),
- International Confederation of
Midwives etc.
c) Related organization and their
contribution to nursing: World Health
Organization, Red cross and St. john’s
Ambulance, Colombo plan, UNICEF,
World Bank etc.
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Observational
visits to State
Nursing Council
and Local TNAI
ofce
Report of visit to
the council
Short answers
Essay type
130
NURSING ADMINISTRATION AND wARD MANAGEMENT
Course Description:-
This course is designed to help the student to understand the basic principles of administration and its
application to the management of ward and health care unit.
General Objective:-
Upon completion of this course, the students shall able to:
1. Describe the meaning and principles of administration.
2. Apply the principles of administration in practice of nursing
3. Plan the nursing service in the ward and community health settings.
4. Describe the importance of good administration in the day to day nursing service in varied health care
setting.
Total Hours: 40
Unit
Learning
Objectives
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
I Describe the
meaning ,
philosophy and
principles of
administration
Introduction
a) Administration and management
- Meaning
- Philosophy
- Elements and principles
- Signicance
4 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
II Describe the
management
process
Management process
a) Planning
- Importance
- Purpose
- Types of planning
b) Organization
- Principles of organization
- Organization chart of hospital/ward/
PHC/ Sub center
c) Stafng
- Scheduling
- Recruitment, selection, deployment,
retaining, promotion, superannuation
- Personnel management
- Job description
- Job specication
- Staff development and staff welfare
d) Directing
e) Co-ordination and control
- Quality management
f) Budgeting
g) Policies of hospital and various
department of the hospital
15 Lecture cum
discussion
Companion of
organization
charts
Short answers
Essay type
Objective type
Written test
Evaluation of
the organization
chart prepared by
students.
131
Unit
Learning
Objectives
Contents Hr
Teaching
learning
activities
Assessment
methods
IV Explain the
administration of
different health
care units
Administration of hospital/department/
unit/ ward
a) Health centre/ unit physical layout
b) Safety measures for prevention of
accidents and infections
c) Legal responsibilities of a nurse
d) Leadership styles
e) Problem solving : process and
approach, steps and methods of dealing
with complaints of patients and other
health team members.
f) Records and reports: meaning, types,
importance.
9 Lecture cum
discussion
Role play
Group work on
physical layout
Reading notes
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
V Discuss the
importance of
maintaining
supplies and
equipment
for effective
administration
Management of equipment supplies.
a)
Maintenance of supplies & equipment
(preventive maintenance)
b) Handing over and taking over of
inventory
c)
Indent and ordering of supplies and
equipment
d) Problem solving : process and
approach, steps and methods of dealing
with supplies and equipment.
7 Lecture cum
discussion
Role play
Group project on
problem solving
Short answers
Objective type
Essay type
Evaluation of the
report on Group
project
VI Discuss the cost
and nancing of
health services in
India
Cost and nancing of health care
a)
Cost of health care
b) Health nancing
c) National health plans (annual and ve
year plans) and outlays, role of state
and central government in allocation of
funds
d) Health insurance- types, issues etc.
5 Lecture cum
discussion
Short answer
Test
132
